CFP: eSports and professional game play
The purpose of this special issue is to investigate the rise of eSports.
Much has happened in the area of professional gaming since the Space Invaders Championship of 1980. We have seen live Internet streaming eclipse televised eSports events, such as on the American show Starcade.
Authors are invited to submit manuscripts that
- Examine the emergence of eSports
- The uses of streaming technology
- Traditions of games that support professional players – chess, go, bridge, poker, league of legends, Dota 2, Starcraft
- Fan perspectives
- Professional player perspectives
- Market analysis
- Meta-analyses of existing research on eSports
- Answer specific questions such as:
- How should game user research examine the emergence of eSports? Should we differentiate pragmatic and hedonic aspects of the game?
- What are the methodologies for conducting research on eSports?
- What is the role of player, the audience, the developer, the venue?
- Case studies, worked examples, empirical and phenomenological, application of psychological and humanist approaches?
- Field research
- Face to face interviewing
- Creation of user tests
- Gathering and organizing statistics
- Define Audience
- User scenarios
- Creating Personas
- Product design
- Feature writing
- Requirement writing
- Content surveys
- Graphic Arts
- Interaction design
- Information architecture
- Process flows
- Usability
- Prototype development
- Interface layout and design
- Wire frames
- Visual design
- Taxonomy and terminology creation
- Copywriting
- Working with programmers and SMEs
- Brainstorm and managing scope (requirement) creep
- Design and UX culture
Potential authors are encouraged to contact Brock R. Dubbels (Dubbels@mcmaster.ca) to ask about the appropriateness of their topic.
Deadline for Submission July 2016.
Authors should submit their manuscripts to the submission system using the following link:
http://www.igi-global.com/authorseditors/titlesubmission/newproject.aspx
(Please note authors will need to create a member profile in order to upload a manuscript.)
Manuscripts should be submitted in APA format.
They will typically be 5000-8000 words in length.
Full submission guidelines can be found at: http://www.igi-global.com/journals/guidelines-for-submission.aspx
Mission – IJGCMS is a peer-reviewed, international journal devoted to the theoretical and empirical understanding of electronic games and computer-mediated simulations. IJGCMS publishes research articles, theoretical critiques, and book reviews related to the development and evaluation of games and computer-mediated simulations. One main goal of this peer-reviewed, international journal is to promote a deep conceptual and empirical understanding of the roles of electronic games and computer-mediated simulations across multiple disciplines. A second goal is to help build a significant bridge between research and practice on electronic gaming and simulations, supporting the work of researchers, practitioners, and policymakers.
What we cannot know or do individually, we may be capable of collectively.
My research examines the transformation of perceptual knowledge into conceptual knowledge. Conceptual knowledge can be viewed as crystallized, which means that it has become abstracted and is often symbolized in ways that do not make the associated meaning obvious. Crystallized knowledge is the outcome of fluid intelligence, or the ability to think logically and solve problems in novel situations, independent of acquired knowledge. I investigate how groups and objects may assist in crystallization of knowledge, or the construction of conceptual understanding.
I am currently approaching this problem from the perspective that cognition is externalized and extended through objects and relationships. Â This view posits that skill, competence, knowledge are learned through interaction aided with objects imbued with collective knowledge.
Groups make specialized information available through objects and relationships so that individual members can coordinate their actions and do things that would be hard or impossible for them to enact individually. To examine this, I use a socio-cognitive approach, which views cognition as distributed, where information processing is imbued in objects and communities and aids learners in problem solving.
This socio-cognitive approach is commonly associated with cognitive ethnography and the study of social networks. In particular, I have special interest in how play, games, modeling, and simulations can be used to enhance comprehension and problem solving through providing interactive learning. In my initial observational studies, I have found that games are structured forms of play, which work on a continuum of complexity:
- Pretense, imagery and visualization of micro worlds
- Tools, rules, and roles
- Branching / probability
Games hold communal knowledge, which can be learned through game play. An example of this comes from the board game Ticket to Ride. In this strategy game players take on the role of a railroad tycoon in the early 1900′s. The goal is to build an empire that spans the United States while making shrewd moves that block your opponents from being able to complete their freight and passenger runs to various cities. Game play scaffolds the learner in the history and implications of early transportation through taking on the role of an entrepreneur and learning the context and process of building up a railroad empire. In the course of the game, concept are introduced, with language, and value systems based upon the problem space created by the game mechanics (artifacts, scoring, rules, and language). The game can be analyzed as a cultural artifact containing historical information; a vehicle for content delivery as a curriculum tool; as well as an intervention for studying player knowledge and decision-making.
I have observed that learners interact with games with growing complexity of the game as a system. As the player gains top sight, a view of the whole system, they play with greater awareness of the economy of resources, and in some cases an aesthetic of play. For beginning players, I have observed the following progression:
- Trial and error – forming a mental representation, or situation model of how the roles, rules, tools, and contexts work for problem solving.
- Tactical trials – a successful tactic is generated to solve problems using the tools, rules, roles, and contexts. This tactic may be modified for use in a variety of ways as goals and context change in the game play.
- Strategies—the range of tactics of resulted in strategies that come from a theory of how the game works. This approach to problem solving indicates a growing awareness of systems knowledge, the purpose or criteria for winning, and is a step towards top sight. They understand that there are decision branches, and each decision branch comes with risk reward they can evaluate in the context of economizing resources.
- Layered strategies—the player is now making choices based upon managing resources because they are now economizing resources and playing for optimal success with a well-developed mental representation of the games criteria for winning, and how to have a high score rather than just finish.
- Aesthetic of play—the player understands the system and has learned to use and exploit ambiguities in the rules and environment to play with an aesthetic that sets the player apart from others. The game play is characterized with surprising solutions to the problem space.
For me, games are a structured form of play. As an example, a game may playfully represent an action with associated knowledge, such as becoming a railroad tycoon, driving a high performance racecar, or even raising a family. Games always involve contingent decision-making, forcing the players to learn and interact with cultural knowledge simulated in the game.
Games currently take a significant investment of time and effort to collectively construct. These objects follow in a history of collective construction by groups and communities. Consider the cartography and the creation of a map as an example of collective distributed knowledge imbued in an object. Â According to Hutchins (1996),
“A navigation chart represents the accumulation of more observations than any one person could make in a lifetime. It is an artifact that embodies generations of experience and measurement. No navigator has ever had,nor will one ever have, all the knowledge that is in the chart.â€
A single individual can use a map to navigate an area with competence, if not expertise. Observing an individual learning to use a map, or even construct one is instructive for learning about comprehension and decision-making. Interestingly, games provide structure to play, just as maps and media appliances provide structure to data to create information. Objects such as maps and games are examples of collective knowledge, and are what Vygotsky termed a pivot.
The term pivot was initially conceptualized in describing children’s play, particularly as a toy. A toy is a representation used in aiding knowledge construction in early childhood development. This is the transition where children may move from recognitive play to symbolic and imaginative play, i.e. the child may play with a phone the way it is supposed to be used to show they can use it (recognitive), and in symbolic or imaginative play, they may pretend a banana is the phone.
This is an important step since representation and abstraction are essential in learning language, especially print and alphabetical systems for reading and other discourse. In this sense, play provides a transitional stage in this direction whenever an object (for example a stick) becomes a pivot for severing meaning of horse from a real horse. The child cannot yet detach thought from object. (Vygotsky, 1976, p 97). For Vygotsky, play represented a transition in comprehension and problem solving –where the child moved from external processing — imagination in action —to internal processing — imagination as play without action.
In my own work, I have studied the play of school children and adults as learning activities. This research has informed my work in classroom instruction and game design. Learning activities can be structured as a game, extending the opportunity to learn content, and extend the context of the game into other aspects of the learner’s life, providing performance data and allowing for self-improvement with feedback, and data collection that is assessed, measured and evaluated for policy.
My research and publications have been informed by my work as a tenured teacher and software developer. A key feature of my work is the importance of designing for learning transfer and construct validity. When I design a learning environment, I do so with research in mind. Action research allows for reflection and analysis of what I created, what the learners experienced, and an opportunity to build theory. What is unique about what I do is the systems approach and the way I reverse engineer play as a deep and effective learning tool into transformative learning, where pleasurable activities can be counted as learning.
Although I have published using a wide variety of methodologies, cognitive ethnography is a methodology typically associated with distributed cognition, and examines how communities contain varying levels of competence and expertise, and how they may imbue that knowledge in objects. I have used it specifically on game and play analysis (Dubbels 2008, 2011). This involves observation and analysis of Space or Context—specifically conceptual space, physical space, and social space. The cognitive ethnographer transforms observational data and interpretation of space into meaningful representations so that cognitive properties of the system become visible (Hutchins, 2010; 1995). Cognitive ethnography seeks to understand cognitive process and context—examining them together, thus, eliminating the false dichotomy between psychology and anthropology. This can be very effective for building theories of learning while being accessible to educators.
My current interest is in the use of cognitive ethnographic methodology with traditional form serves as an opportunity to move between inductive and deductive inquiry and observation to build a Nomological network (Cronbach & Meehl, 1955) using measures and quantified observations with the Multiple Trait and Multiple Method Matrix Analysis (Campbell & Fiske, 1959) for construct validity (Cook & Campbell, 1979; Campbell & Stanley, 1966) especially in relation to comprehension and problem solving based upon the Event Indexing Model (Zwaan & Radvansky, 1998).
We distribute knowledge because it is impossible for a single human being, or even a group to have mastery of all knowledge and all skills (Levy, 1997). For this reason I study access and quality of collective group relations and objects and the resulting comprehension and problem solving. The use of these objects and relations can scaffold learners and inform our understanding of how perceptual knowledge is internalized and transformed into conceptual knowledge through learning and experience.
Specialties
Educational research in cognitive psychology, social learning. identity, curriculum and instruction, game design, theories of play and learning, assessment, instructional design, and technology innovation.
Additionally:
The convergence of media technologies now allow for collection, display, creation, and broadcast of information as narrative, image, and data. This convergence of function makes two ideas important in the study of learning:
- The ability to create of media communication through narrative, image, and data analysis and information graphics is becoming more accessible to non-experts through media appliances such as phones, tablets, game consoles and personal computers.
- These media appliances have taken very complex behaviors such as film production, which in the past required teams of people with special skill and knowledge, and have imbued these skills and knowledge in hand-held devices that are easy to use, and are available to the general population.
- This accessibility allows novices to learn complex media production, analysis, and broadcast, and allows for the study of these devices as object that has been imbued with the knowledge and skill, as externalized cognitionThrough the use of these devices, the general population may learn complex skills and knowledge that may have required years of specialized training in the past. Study of the interaction between of individuals learning to use these appliances and devices can be studied as a progression of internalizing knowledge and skill imbued in objects.
- The convergence of media technologies into small, single–even handheld—devices emphasizes that technology for producing media may change, but the narrative has remained relatively consistent.
- This consistency of media as narrative, imagery, and data analysis emphasizes the importance of the continued study of narrative comprehension and problem solving through the use of these media appliances.
I am concerned that Gamefication obfuscates the real issue in learning:
Transfer.
Is there evidence that game-based learning leads to far transfer?
Without learning transfer, it doesn’t matter how a person learned–whether from a piece of software, watching an expert, rote memorization, or the back of cereal box. What is important is that learning occurred, and how we know that learning occurred.
This leads to issues of assessment and evaluation.
Transfer and Games:Â How do we assess this?
The typical response from gameficators is that assessment does not measure the complex learning from games. I have been there and said that. Â But I have learned that is overly dismissive of assessment and utterly simplistic. As I investigated assessment and psychometrics, I have learned how simplistic were my statements. Games themselves are assessment tools, and I learned that by learning about assessment.
This Gameficator–(yes I am now going to 3rd person)–had to seek knowledge beyond his ludic and narratological powers. He had to learn the mysteries and great lore of psychometrics, instructional design, and educational psychology. It was through this journey into the dark arts, that he has been able to overcome some of the traps of Captain Obvious, and his insidious powers to sidetrack and obfuscate through jargonification,and worse–like taking credit for previously documented phenomena by imposing a new name. . . kind of like my renaming Canada to the now improved, muchmorebetter name: Candyland.
In reality, I had to learn the language and content domain of learning to be an effective instructional designer, just as children learn the language and content domains of science, literature, math, and civics.
What I have learned through my journey, is that if a learner cannot explain a concept, that this inability to explain and demonstrate may be an indicator that the learning from the game experience is not crystallized–that the learner does not have a conceptual understanding that can be explained or expressed by that learner.
Do games deliver this?
Does gamefied learning deliver this?
Gameficators need to address this if this is to be more than a captivating trend.
I am fearful that the good that comes from this trend will not matter if we are only creating  jargonification (even if it is more accessible). It is not enough to redescribe an established instructional design technique if we cannot demonstrate its effectiveness.  We should be asking how learning in game-like contexts enhances learning and how to measure that.
 Measurement and testing are important because well-designed tests and measures can deliver an assessment of crystallized knowledge–does the learner have a chunked conceptual understanding of a concept, such as “resistance”, “average”, “setting”?
Measurement and testing are important because well-designed tests and measures can deliver an assessment of crystallized knowledge–does the learner have a chunked conceptual understanding of a concept, such as “resistance”, “average”, “setting”?
Sure, students may have a gist understanding of a concept. The teacher may even see this qualitatively, but the student cannot express it in a test. So is that comprehension? I think not. The point of the test is an un-scaffolded demonstration of comprehension.
Maybe the game player has demonstrated the concept of “resistance” in a game by choosing a boat with less resistance to go faster in the game space– but this is not evidence that they understand the term conceptually. This example from a game may be an important aspect of perceptual learning, that may lead to the eventual ability to explain (conceptual learning); but it is not evidence of comprehension of “resistance” as a concept.
So when we look at game based learning, we should be asking what it does best, not whether it is better. Games can become a type of assessment where contextual knowledge is demonstrated. But we need to go beyond perceptual knowledge–reacting correctly in context and across contexts–to conceptual knowledge: the ability to explain and demonstrate a concept.
My feeling is that one should be skeptical of Gameficators that pontificate without pointing to the traditions in educational research. If Gamefication advocates want to influence education and assessment, they should attempt to learn the history, and provide evidential differences from the established terms they seek  to replace.
A darker shadow is cast
Another concern I have is that  perhaps not all gameficators are created equal. Maybe some gameficators are not really advocatingfor the game elements that are really fundamental aspects of games? Maybe there are people with no ludic-narratological powers donning the cape of gamefication! I must ask, is this leaderboard what makes for “gameness”? Or does a completion task-bar make for gamey experience?
Maybe there are people with no ludic-narratological powers donning the cape of gamefication! I must ask, is this leaderboard what makes for “gameness”? Or does a completion task-bar make for gamey experience?
Does this leaderboard for shoe preference tell us anything but shoe preference? Where is the game?
Are there some hidden game mechanics that I am failing to apprehend?
Is this just villainy?
Here are a couple of ideas that echo my own concerns:
It seems to me, that:
- some of the elements of gamefication rely heavily on aspects of games that are not new, just rebranded.
- some of the elements of gamefication aren’t really “gamey”.
What I like about games is that games can provide multimodal experiences, and provide context and prior knowledge without the interference of years of practice-this is new. Games accelerate learning by reducing the some of the gatekeeping issues. Now a person without the strength, dexterity and madness can share in some of the experience of riding skateboard off a ramp.  The benefit of games may be in the increased richness of a virtual interactive experience,  and provide the immediate task competencies without the time required to become competent. Games provide a protocol, expedite, and scalffold players toward a fidelity of conceptual experience.
For example, in RIDE, the player is immediately able to do tricks that require many years of practice because the game exaggerates the fidelity of experience. Â This cuts the time it might take to develop conceptual knowledge but reducing the the necessity of coordination, balance, dexterity and insanity to ride a skateboard up a ramp and do a trick in the air and then land unscathed.
Gameficators might embrace this notion.
Games can enhance learning in a classroom, and enhance what is already called experiential learning.
My point:
words, terms, concepts, and domain praxis matter.
Additionally, we seem to be missing the BIG IDEA:
- that the way we structure problems is likely predictive of a successful solutionHerb Simon expressed the idea in his book The Sciences of the Artificial this way:
“solving a problem simply means representing it so as to make the solution transparent.” (1981: p. 153)
Games can help structure problems.
But do they help learners understand how to structure a problem. Do they deliver conceptualized knowledge? Common vocabulary indicative of a content domain?
The issue is really about What Games are Good at Doing, not whether they are better than some other traditional form of instruction.
Do they help us learn how to learn? Do they lead to crystallized conceptual knowledge that is found in the use of common vocabulary? In physics class, when we mention “resistance”, students should offer more than
“Resistance is futile”
or, a correct but non-applicable answer such as “an unwillingness to comply”.
The key is that the student can express the expected knowledge of the content domain in relation to the word. This is often what we test for. So how do games lead to this outcome?
I am not hear to give gameficators a hard time–I have a gamefication badge (self-created)–but I would like to know that when my learning is gamefied that the gameficator had some knowledge from the last century of instructional design and learning research, just as I want my physics student to know that resistance as an operationalized concept in science, not a popular cultural saying from the BORG.
The concerns expressed here are applicable in most learning contexts. But if we are going to advocate the use games, then perhaps we should look at how good games are effective, as well as how good lessons are structured. Perhaps more importantly,
- we may need to examine our prevalent misunderstandings about learning assessment;
- perhaps explore the big ideas and lessons that come from years educational psychology research, rather than just renaming and creating new platform without realizing or acknowledging, that current ideas in gamefication stand on the established shoulders of giants from a century of educational research.
Jargonification is a big concern. So lets make our words matter and also look back as we look forward. Games are potentially powerful tools for learning, but not all may be effective in every purpose or context. What does the research say?
I am hopeful gamefication delivers a closer look at how game-like instructional design may enhance successful learning.
I don’t think anyone would disagree — fostering creativity should be a goal of classroom learning.
However, the terms creativity and innovation are often misused. When used they typically imply that REAL learning cannot be measured. Fortunately, we know A LOT about learning and how it happens now. It is measurable and we can design learning environments that promote it. It is the same with creativity as with intelligence–we can promote growth in creativity and intelligence through creative approaches to pedagogy and assessment. Because data-driven instruction does not kill creativity, it should promote it.
One of the ways we might look at creativity and innovation is through the much maligned tradition of intelligence testing as described in the Wikipedia:
Fluid intelligence or fluid reasoning is the capacity to think logically and solve problems in novel situations, independent of acquired knowledge. It is the ability to analyze novel problems, identify patterns and relationships that underpin these problems and the extrapolation of these using logic. It is necessary for all logical problem solving, especially scientific, mathematical and technical problem solving. Fluid reasoning includes inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning, and is predictive of creativity and innovation.
Crystallized intelligence is indicated by a person’s depth and breadth of general knowledge, vocabulary, and the ability to reason using words and numbers. It is the product of educational and cultural experience in interaction with fluid intelligence and also predicts creativity and innovation.
The Myth of Opposites
Creativity and intelligence are not opposites. It takes both for innovation.
What we often lack are creative ways of measuring learning growth in assessments. When we choose to measure growth in summative evaluations and worksheets over and over , we nurture boredom and kill creativity.
To foster creativity, we need to adopt and implement pedagogy and curriculum that promotes creative problems solving, and also provides criteria that can measure creative problem solving.
What is needed are ways to help students learn content in creative ways through the use of creative assessments.
We often confuse the idea of  learning creatively with trial and error and play, free of any kind of assessment–that somehow the Mona Lisa was created through just free play and doodling. That somehow assessment kills creativity.  Assessment provide learning goals.
Without learning criteria, students are left to make sense of the problem put before them with questions like “what do I do now?” (ad infinitum).
The role of the educator is to design problems so that the solution becomes transparent. This is done through providing information about process, outcome, and quality criteria . . . assessment, is how it is to be judged. For example, “for your next assignment, I want a boat that is beautiful and  that is really fast. Here are some examples of boats that are really fast.  Look at the hull, the materials they are made with, etc. and design me a boat that goes very fast and tell me why it goes fast. Tell me why it is beautiful.” Now use the terms from the criteria. What is beautiful? Are you going to define it? How about fast? Fast compared to what? These open-ended, interest-driven, free play assignments might be motivating, but they lead to quick frustration and lots of “what do I do now?”
But play and self-interest arte not the problem here. The problem is the way we are approaching assessment.
Although play is described as a range of voluntary, intrinsically motivated activities normally associated with recreational pleasure and enjoyment; Pleasure and enjoyment still come from judgements about one’s work–just like assessment–whether finger painting or creating a differential equation. The key feature here is that play seems to involve self-evaluation and discovery of key concepts and patterns. Assessments can be constructed to scaffold and extend this, and this same process can be structured in classrooms through assessment criteria.
Every kind of creative play activity has evaluation and self-judgement: the individual is making judgements about pleasure, and often why it is pleasurable. This is often because they want to replicate this pleasure in the future, and oddly enough, learning is pleasurable. So when we teach a pleasurable activity, the learning may be pleasurable. This means chunking the learning and concepts into larger meaning units such as complex terms and concepts, which represent ideas, patterns, objects, and qualities. Thus, crystallized intelligence can be constructed through play as long as the play experience is linked and connected to help the learner to define and comprehend the terms (assessment criteria). So when the learner talks about their boat, perhaps they should be asked to sketch it first, and then use specific terms to explain their design:
Bow is the frontmost part of the hull
Stern is the rear-most part of the hull
Port is the left side of the boat when facing the Bow
Starboard is the right side of the boat when facing the Bow
Waterline is an imaginary line circumscribing the hull that matches the surface of the water when the hull is not moving.
Midships is the midpoint of the LWL (see below). It is half-way from the forwardmost point on the waterline to the rear-most point on the waterline.
Baseline an imaginary reference line used to measure vertical distances from. It is usually located at the bottom of the hull
Along with the learning activity and targeted learning criteria and content, the student should be asked a guiding question to help structure their description.
So, how do these parts affect the performance of the whole?
Additionally, the learner should be adopting the language (criteria) from the rubric to build comprehension. Taking perception, experience, similarities and contrasts to understand Bow and Stern, or even Beauty.
Experiential Learning for Fluidity and Crystallization
What the tradition of intelligence offers is an insight as to how an educator might support students. What we know is that intelligence is not innate. It can change through learning opportunities. The goal of the teacher should be to provide experiential learning that extends Fluid Intelligence, through developing problem solving, and link this process to crystallized concepts in vocabulary terms that encapsulate complex process, ideas, and description.
The real technology in a 21st Century Classroom is in the presentation and collection of information. It is the art of designing assessment for data-driven decision making. The role of the teacher should be in grounding crystallized academic concepts in experiential learning with assessments the provide structure for creative problem solving. The teacher creates assessments where the learning is the assessment. The learner is scaffolded through the activity with guidance of assessment criteria.
A rubric, which provides criteria for quality and excellence can scaffold creativity innovation, and content learning simultaneously. A well-conceived assessment guides students to understand descriptions of quality and help students to understand crystallized concepts.
An example of a criteria-driven assessment looks like this:
| Purpose & Plan | Isometric Sketch | Vocabulary | Explanation | |
| Level up | Has identified event and hull design with reasoning for appropriateness. | Has drawn a sketch where length, width, and height are represented by lines 120 degrees apart, with all measurements in the same scale. | Understanding is clear from the use of five key terms from the word wall to describe how and why the boat hull design will be successful for the chosen event. | Clear connection between the hull design, event, sketch, and important terms from word wall and next steps for building a prototype and testing. |
| Approaching | Has chosen a hull that is appropriate for event but cannot connect the two. | Has drawn Has drawn a sketch where length, width, and height are represented. | Uses five key terms but struggles to demonstrate understanding of the terms in usage. | Describes design elements, but cannot make the connection of how they work together. |
| Do it again | Has chosen a hull design but it may not be appropriate for the event. | Has drawn a sketch but it does not have length, width, and height represented. | Does not use five terms from word wall. | Struggles to make a clear connection between design conceptual design stage elements. |
What is important about this rubric is that it guides the learner in understanding quality and assessment. It also familiarizes the learner with key crystallized concepts as part of the assessment descriptions. In order to be successful in this playful, experiential activity (boat building),  the learner must learn to comprehend and demonstrate knowledge of the vocabulary scattered throughout the rubric such as: isometric, reasoning, etc. This connection to complex terminology grounded with experience is what builds knowledge and competence. When an educator can coach a student connecting their experiential learning with the assessment criteria, they construct crystallized intelligence through grounding the concept in experiential learning, and potentially expand fluid intelligence through awareness of new patterns in form and structure.
Play is Learning, Learning is Measurable
Just because someone plays, or explores does not mean this learning is immeasurable. The truth is, research on creative breakthroughs demonstrate that authors of great innovation learned through years of dedicated practice and were often judged, assessed, and evaluated.  This feedback from their teachers led them to new understanding and new heights. Great innovators often developed crystallized concepts that resulted from experience in developing fluid intelligence. This can come from copying the genius of others by replicating their breakthroughs; it comes from repetition and making basic skills automatic, so that they could explore the larger patterns resulting from their actions. It was the result of repetition and exploration, where they could reason, experiment, and experience without thinking about the mechanics of their actions.  This meant learning the content and skills from the knowledge domain and developing some level of automaticity. What sets an innovator apart it seems, is tenacity and being playful in their work, and working hard at their play.
According to Thomas Edison:
During all those years of experimentation and research, I never once made a discovery. All my work was deductive, and the results I achieved were those of invention, pure and simple. I would construct a theory and work on its lines until I found it was untenable. Then it would be discarded at once and another theory evolved. This was the only possible way for me to work out the problem. … I speak without exaggeration when I say that I have constructed 3,000 different theories in connection with the electric light, each one of them reasonable and apparently likely to be true. Yet only in two cases did my experiments prove the truth of my theory. My chief difficulty was in constructing the carbon filament. . . . Every quarter of the globe was ransacked by my agents, and all sorts of the queerest materials used, until finally the shred of bamboo, now utilized by us, was settled upon.
On his years of research in developing the electric light bulb, as quoted in “Talks with Edison” by George Parsons Lathrop in Harpers magazine, Vol. 80 (February 1890), p. 425
So when we encourage kids to be creative, we must also understand the importance of all the content and practice necessary to creatively breakthrough. Edison was taught how to be methodical, critical, and observant. He understood the known patterns and made variations. It is important to know the known forms to know the importance of breaking forms. This may inv0lve copying someone else’s design or ideas. Thomas Edison also speaks to this when he said:
Everyone steals in commerce and industry. I have stolen a lot myself. But at least I know how to steal.
Edison stole ideas from others, (just as Watson and Crick were accused of doing). The point Watson seems to be making here is that he knew how to steal, meaning, he saw how the parts fit together. He may have taken ideas from a variety of places, but he had the knowledge, skill, and vision to put them together. This synthesis of ideas took awareness of the problem, the outcome, and how things might work. Lots and lots of experience and practice.
To attain this level of knowledge and experience, perhaps stealing ideas, or copying and imitation are not a bad idea for classroom learning? However copying someone else in school is viewed as cheating rather than a starting point. Perhaps instead, we can take the criteria of examples and design classroom problems in ways that allow discovery and the replication of prior findings (the basis of scientific laws). It is often said that imitation is the greatest form of flattery. Imitation is also one of the ways we learn. In the tradition of play research, mimesis is imitation–Aristotle held that it was “simulated representation”.
The Role of Play and Games
In close, my hope is that we not use the terms “creativity” and “innovation” as suitcase words to diminish such things as minimum standards. We need minimum standards.
But when we talk about teaching for creativity and innovation, where we need to start is the way that we gather data for assessment. Often assessments are unimaginative in themselves. They are applied in ways that distract from learning, because they have become the learning. One of the worst outcomes of this practice is that students believe that they are knowledgeable after passing a minimum standards test. This is the soft-bigotry of low expectation. Assessment should be adaptive, criteria driven, and modeled as a continuous improvement cycle.
This does not mean that we must  drill and kill kids in grinding mindless repetition. Kids will grind towards a larger goal where they are offered feedback on their progress. They do it in games.
Games are structured forms of play. They are criteria driven, and by their very nature, games assess, measure, and evaluate. But they are only as good as their assessment criteria.
These concepts should be embedded in creative active inquiry that will allow the student to embody their learning and memory. However, many of the creative, inquiry-based lessons I have observed tend to ignore the focus of academic language–the crystallized concepts. Such as, “what is fast?”, “what is beauty”, Â “what is balance?”, or “what is conflict?” The focus seems to be on interacting with content rather than building and chunking the concepts with experience. When Plato describes the world of forms, and wants us to understand the essence of the chair, i.e., “what is chairness?” We may have to look at a lot of chairs to understand chairness. Â Bu this is how we build conceptual knowledge, and should be considered when constructing curriculum and assessment. A guiding curricular question should be:
How does the experience inform the concepts in the lesson?
There is a way to use data-driven instruction in very creative lessons, just like the very unimaginative drill and kill approach. Teachers and assessment coordinators need to take the leap and learn to use data collection in creative ways in constructive assignments that promote experiential learning with crystallized academic concepts.
If you have kids make a diorama of a story, have them use the concepts that are part of the standards and testing: Plot, Character, Theme, Setting, ETC. Make them demonstrate and explain. If you want kids to learn the physics have them make a boat and connect the terms through discovery. Use their inductive learning and guide them to conceptual understanding.This can be done through the use of informative assessments, such as with rubrics and scales for assessment.  Evaluation and creativity are not contradictory or mutually exclusive. These seeming opposites are complementary, and can be achieved through embedding the crystallized, higher order concepts into meaningful work.
 Why Video Games Sustain Engagement: A Cage Match between Social Learning Theories
Why Video Games Sustain Engagement: A Cage Match between Social Learning Theories
Brock Dubbels
The Center for Cognitive Sciences
Department of Curriculum & Instruction
The University of Minnesota
Abstract: Although games are seen as high interest activities, many children buy them, play them, and move on to another activity. This represents a challenge in creating instructional interventions to achieve an educational outcome or a training effect. This study was conducted to inform an after school program designed to deliver a training effect on female adolescent health. To investigate this, a small sample of young female experts were recruited and interviewed for rich phenomenological descriptions (van Manen, 2002) to examine the aspects engagement as described by (Chapman 2006) as informed through identity construction (Buckingham, 2007, Van Gennep, 1960; Turner, 1969). Interview transcripts were coded and analyzed using methods from discourse analysis (Gee, 1992, 1996, 1999; Fairclough, 2007) using themes from social learning theories such as Communities of Practice (Wenger, 1996), Affinity Groups (Gee, 2001), Positive Interdependence (Deutsch, 1962, Johnson & Johnson, 1989), and Self-Determination (Ryan and Deci, 2008). Implications of this study include understanding the importance of identity construction to motivate and sustain engagement in learning.
Key terms: Dance Dance Revolution, Phenomenology, Identity Construction, Self-Determination Theory, Affinity Groups, Motivation, Engagement, Social Learning, Instructional Design, Rites of Passage, Play, Games, Initiation, Semiotic Domains, Apprenticeship, Transformation.
Citation:
Dubbels, B.R. (2010) Designing Learning Activities for Sustained Engagement — Four Social Learning Theories Coded and Folded into Principals for Instructional Design through Phenomenological Interview and Discourse Analysis. In Discoveries in Gaming Research. IGI Global Publishers.
Introduction
This article seeks to understand what engages young people in learning, and what sustains their interest to continue. It was intended to explore the elements that inform the lived experience of a chosen play activity and examine the possible social learning theories that might inform it. Five social learning theories were examined to ground the aspects engagement as described by (Chapman 2006) and informed through social learning theories such as Communities of Practice (Wenger, 1996), Affinity Groups (Gee, 2001), Positive Interdependence (Deutsch, 1962, Johnson & Johnson, 1989), and Self-Determination (Ryan and Deci, 2008). Implications of this study include understanding the importance of identity construction to motivate and sustain engagement in learning (Buckingham, 2007, Van Gennep, 1960; Turner, 1969).
All of the theories listed above seek to explain the motivation behind learning as socially constructed and distributed phenomena; all seek to describe the process of identity construction as an impetus for situated learning. The assumption in this study was that it is through the process of identity construction that engagement is sustained and supported through the process of group affiliation and is distributed through apprenticeship, modeling, and group interaction.
| Social Learning Theory | Scale/Application | Author(s) |
| Engagement | Aggregate | Chapman, 2006 |
| Communities of Practice | Structural Social | Wenger, 1996 |
| Positive Interdependence | Structural Social | Deutsch, 1962, Johnson & Johnson, 1989; Johnson and Holubec, 1998), |
| Affinity Groups | Structural Social | Gee, 2001 |
| Self-Determination | Social Psychological | Deci and Ryan, 2008 |
Identity construction may be an organizing principle in understanding motivation and engagement, and yet these social learning theories do not present themselves as descriptions of the identity construction process, but rather focus on structural factors in relationships Community (Wenger, 1998), (Deutsch, 1962, Johnson & Johnson, 1989; Johnson, Johnson and Holubec, 1998), Activity (Gee, 2001), and needs of the individual (Deci and Ryan, 2008) as organizing principles. For the purposes of this study, these theories were operationalized to provide insight for designing instructional environments that will motivate and sustain the engagement of the learner. It was predicted that identity construction would predict motivation and engagement. This prediction was based upon the recurrence of the theme throughout the social learning theories. The act of identity construction is an act of becoming, Not only do individuals construct a unique description of themselves as an identity, but it I also conferred upon them and reinforced through context, including age, personal history, relationships and history, location, and community status.
Identity construction rituals and rites of passage
Traditionally, communities gather to provide ceremony for initiation and status transition for such things as the celebration of status change from child to adult; initiation single people to married couple; and a multitude of culturally mediated roles, acknowledgement, and transitions. Although there may be many more transitions and ritual’s in today’s society because of the great variety of cultural subgroups, i.e. churches, car clubs, self-help groups like Alcoholic Anonymous, and hobby groups like The Peoples’ Revolutionary Knitting Circle, etc.; many of these groups traditionally necessitated face to face interaction, but with the internet and today’s computing power, these relations can be mediated digitally through portals such as Facebook, Xbox Live, Second Life, and other social networking tools.
The Dance Dance Revolution game club might be represented as a ritual rite of passage to understand how and why people build identities around their play, and sustain engagement to ultimately develop expertise. Central to the rite of passage is the initiation ritual (Van Gennep, 1960), where new roles and status are conferred through public performance where play, the subjunctive mood (Turner, 1969), situates the activity, so that rules, roles, and consequences are suspended and participants can explore new identities, associated activities, and their semiotic domains and develop new status.
With this in mind, video games may represent new forms of the rite of passage and initiation ritual; games are structured activities that are valued by certain cultural sub-groups, represent expert systems that resemble apprenticeship activities, involve performance initiation, and with similar emphasis on what Sutton-Smith (1976) called the play ethos. The ethos is the context and purpose of the activity. It is as the expectation of consequence of an activity performed. It is the context where play is the subjunctive mood. The subjunctive mood observed in games and ritual are said to decontextualize the action and provide a suspension of rules, roles, and consequences found in ordinary life to allow for the exploration of new identities, rules, roles, actions, and social affiliations and status in a safe space.
Purpose of study
This interview was to inform design features to develop a program for pre-adolescent exercise with Dance Dance Revolution for the study of obesity reduction and increasing bone density. The study was also intended to get a sense of why a young woman sustained engagement with Dance Dance Revolution over three years to develop expertise, and how educators might replicate that kind of commitment to learning and practice.
Background of the study
Health care professionals have observed an increase in levels of childhood obesity. This increase has been attributed in large part to physical inactivity. Physical inactivity not only leads to obesity and poor cardiovascular health, it also has negative effects on bone health. Bones function to support a mechanical load (a force exerted by body weight, muscle, growth, or activity). Bone is constantly formed and reabsorbed throughout life in a generally balanced way. However, in a three- to four-year window during puberty, bone formation is accelerated. In that period, as much bone material is deposited as will be lost during a person’s entire adult life. During these pivotal years of bone development, physical activity is important for optimizing bone health, as it has been shown to reduce the incidence of fractures later in life.
Because it is difficult to motivate children to participate in the type of cardiovascular activities that adults engage in (running, cycling, aerobics), new strategies must be developed, and these may demand elements that            motivate the learner to sustain engagement over a longer period of time in order to promote and sustain life habits for physical conditioning.
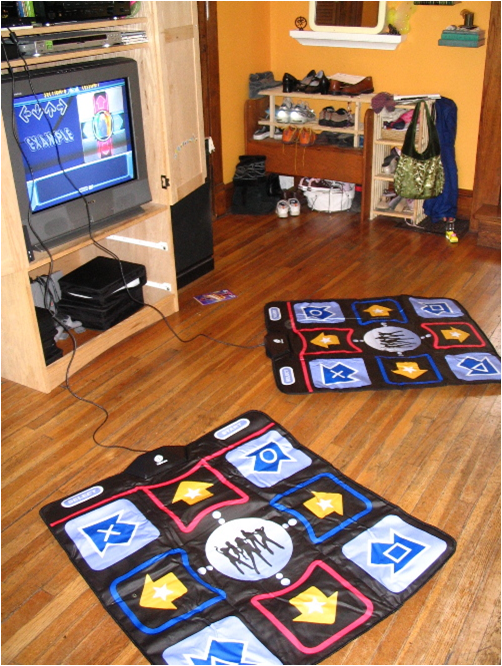
Dance Dance Revolution is not your typical video game.
The video dance game Dance Dance Revolution may be a possible solution to increasing activity and mechanical load because of the amount of jumping activity, but the young person must be motivated to start, and engagement must be sustained for the activity to produce valid and reliable measures of obesity and bone density.
The issue under investigation is how to help young people start an activity and sustain it; the
simple answer to this was, seemingly, to make it fun; to make it a high-interest activity; but many toys, games, and activities are often tried once and then put aside. What came out of the interview was:
- the importance of aligning the outcomes with a desirable activity,
- the importance of group and environment to the construction of status and identity that makes belonging to a group desirable;
- allow for status and relation for reinforcement;
- the centrality of ritual and rites of passage in group performance,
- autonomy supporting environments,
- and again the importance of identity construction for transformation to instantiate sustained engagement conveyed through affiliation, apprenticeship, and expertise.
Interviewee/ informant
To explore this, we recruited Ellen as a DDR expert and possible employee to lead an after school program at one of our sites at the Minneapolis Public Schools. We had posted a hiring description for DDR experts and we had a number of responses; one respondent, Charles, shared that he had a lot of friends who were really good at DDR, and Ellen was listed as one of those people. Ellen came into the lab to show us her DDR play, and we were impressed with her expertise.
What was interesting about Ellen was that she was not from a subversive or reactionary sub-culture. Ellen is part of one of the least studied cultural sub-group in schools (Buckingham, 2007)—an urban, middle class teen that is successful in school, is respectful to teachers, has a part-time job, plays varsity soccer, traveling band, is part of the International Baccalaureate Program, and has a satisfying home life.
These elements of her identity were surprising. We usually assume that video game players are a disenfranchised fringe group at school who do not engage with the typical academic fare. But Ellen was able to balance not only her academics and music instruction, work a part-time job, but also play sports and have friendships. These elements of balance were enticing and we wanted to know how she was doing it so that we might try and replicate not only the physical health benefits in our bone density study, but also some of the psycho-social and affective elements necessary for sustaining engagement (Chapman 2006) —she seemed like a great role model for creating a curriculum that would rely heavily on identity development and she was an intriguing informant to help us understand how play identities might lead to work habits to form healthy minds and bodies.
Methodology and review of literature
The question driving this investigation is “why did she sustain engagement in learning?â€
According to Chapman (2006), engagement is more than behavioral time on task. When looking to measure growth or change, or even to understand whether a learner has truly engaged, an educator should also look for evidence of commitment and positive attitudes related to the activity and subject matter.
- Engagement is not just doing the work, it is a connection and an affinity to an activity supported from the affective domains (Chapman, 2003).
- Skinner & Belmont (1993, p.572) report that engaged learners show sustained behavioral involvement in learning activities accompanied by a positive emotional tone and select tasks at the border of their competencies, initiate action when given the opportunity, and exert intense effort and concentration.
- Pintrich and & De Groot (1990, in Chapman) see engagement as having observable cognitive components that can be seen or elicited through exploring the learner’s use of strategy, metacognition, and self-regulatory behavior to monitor and guide the learning processes.
These attributes do not magically appear in an activity because a student is told that it is good for them, and that they should commit to their betterment; Least likely is that they do it because we threaten, or because just because we want them to. A student must make a choice to commit to an activity and have that commitment reaffirmed over time to sustain engagement. True engagement in an activity is in some sense transformative and resembles identity construction, in that it changes who we are through cognitive, affective, and behavioral elements; but it seems likely that without positive reinforcement (Skinner, 1938) the behavior may result in extinction and the game becomes another resident on the island of misfit toys.
Dance Dance Revolution is considered a high interest activity for many young people, and it does have a reward system that gives real time feedback on performance with rewards for successful play; but without aligning those rewards and achievement with social capital, they lack meaning and status, and the reinforcement system remains a token economy (Ferster and Skinner, 1957) whose tokens are unredeemable. Since these flashing lights and high scores do not buy cars, cell phones and other tokens of esteem for young teens, it seems reasonable that gaining status and respect in a desirable community may provide the value that accompanies success and sustains engagement.
The work of Buckingham on identity development may provide some insight for connecting identity with purpose, motivation, and sustained engagement. Buckingham (2008, p. 3) states that:
Identity is developed by the individual, but it has to be recognized and
confirmed by others. Adolescence is also a period in which young people
negotiate their separation from their family, and develop independent
social competence (for example through participation in “cliquesâ€Â and
larger “crowds†of peers, who exert different kinds of influence).
Identity and status were traditionally conferred through rites of passage, and there may have been many culturally specific instances of these rites for different groups and related activities. Video games may represent a new wrinkle in the way that we enact and view rites of passage–games may offer a form of guided, ritualized behavior for identity construction and group affiliation as an autonomy supporting environment (Ryan & Deci, 1999), Affinity Group (Gee, 2001), or Community of Practice (Wenger, 1998).
A rite of passage does not need to resemble the tribal practices that led to vision quests, ritual markings, or exodus. A rite of passage may be organized in three forms: the process of separation, transition, and integration, (Van Gennep, 1960), but all three of these rites may also be presented as single rite (Barnard and Spencer, 1996). What is important for Van Gennep is the idea of Liminality, or the threshold. In the context of Liminality, the activity space may be far removed from reality, and roles, rules, tools, values, and status may be situated in the flux of play as if a hybrid or interstitial space (Turner, 1969). This concept of the threshold and liminality seems to validate Geertz (1972) and his description of the “Center Bet” in describing the ritual of Balinese Cockfighting and Benthams’ concept of Deep Play. According to Turner (1969), there may be many rites of passage in a person’s life through sub-cultural affiliation (Cock Fighting, DDR, First Job) where identity and entitlement are inculcated through desire to become a respected an acknowledged group member, where they can share in and contribute to group activity, participate in group spaces, and publicly perform renewing and furthering status.
Since identity is conferred from others, there are factors that can identify a person as a group member and as having identity markings. For Gee (2001), the activity is primary and provides the motivation, the source of group membership and markings; and this membership comes about from engagement in active communal practice that centers on the activity; the ancillary relationships stem from the interaction related to the activity. He states that these communities and spaces are hard to identify without knowing the person’s intentions — exactly why people are there. Whether a person actually claims group membership or is acknowledged can be difficult. For Gee, group membership may not be acknowledged or claimed, but attributes can still be observed. The role of Gee’s work is central to operationalizing identity and group membership through offering observable sociocultural markers that come from the semiotic domains as evidence of group membership.
A semiotic domain recruits one or more modalities (e.g., oral or written language,
images, equations, symbols, sounds, gestures, graphs, artifacts, and so forth) to
communicate distinctive types of messages. By the word “fluent†I mean that the
learner achieves some degree of mastery, not just rote knowledge. . . Semiotic
domains are, of course, human creations. As such, each and every one of them is
associated with a group of people who have differentially mastered the domain, but
who share norms, values, and knowledge about what constitutes degrees of mastery
in the domain and what sorts of people are, more or less, “insiders†or “outsidersâ€.
Such a group of people share a set of practices, a set of common goals or endeavors,
and a set of values and norms, however much each of the individuals in the group may
also have their own individual styles and goals, as well as other affiliations.
Gee (2001, pg. 2).
This work allows for certain attributes of group membership to be observable rather than subjective. A young person may have grown up participating in an activity with parents and young friends, but during the puberty years, may reject that affiliation based upon new goals for group membership. A new group may be more desirable than a current group, and the young person may cast of markings that identify them with the old group such as a hat from a uniform, ways of speaking, values, etc. This does not mean that markings of prior group membership with parents, family, and childhood affiliations are not still observable. For Gee it is the activities and the group practices that provide evidence of social learning and group membership from semiotic domains, and it is activity that is central to identity construction.
For Wenger, (1998) identity is central to human learning; identity construction and learning are distributed through community and relations; learning is socially constructed; and motivation is based on a desire for sharing and participatory culture. The work of Wenger shares many attributes with Gee’s work, but the focus for Wenger was on socially distributed cognition and learning as social participation. Earlier work explored the role of learning in apprenticeship, where newcomers would enter into a space where learning was situated and contextualized, and goals and purpose were evident due to entering the space. One entered the space to gain apprenticeship and attempt to acquire and learn the sociocultural practices of the community. Thus the individual is drawn to the group and begins to engage and learn by finding their role in a distributed, networked, cultural-cognitive process with the purpose of the individual as an active participant in the practices of a social community. This participation leads to the construction of his/her identity through these communities. From this understanding develops the concept of the community of practice: a group of individuals participating in communal activity– creating their shared identity through engaging in and contributing to the practices of their communities.
The difficulty with this theory is that group membership is hard to define. A person may want to be part of group and claim group membership, but not have the identifiable characteristics that define the membership, but it did lay the groundwork for many of the same features of Gee’s construct.
For Deci and Ryan (2008) these same attributes are also shared, but the focus of Self-Determination Theory comes from work on motivation with a focus on Autonomy — possibly built from early work by White (1959) where organisms have an innate need to experience competence, and experience joy and pleasure with the new behaviors when they assert competence over the environment.—what he called effectance motivation.
For Ryan and Deci motivation is based on the degree that an activity or value has been internalized, and this is based upon the degree to which the behavior has meaning within the context of the arena of performance. In this sense, the feelings of relatedness and belonging in a social, or group setting, play a part in the internalization process along with an inherent desire for competence and autonomy. In order to feel belonging and relatedness, an individual develops autonomy through competence and creates the identity for relatedness and belonging. This process can happen from belonging to competence to autonomy, or other sequences. The key motivating factor for Deci and Ryan is autonomy.
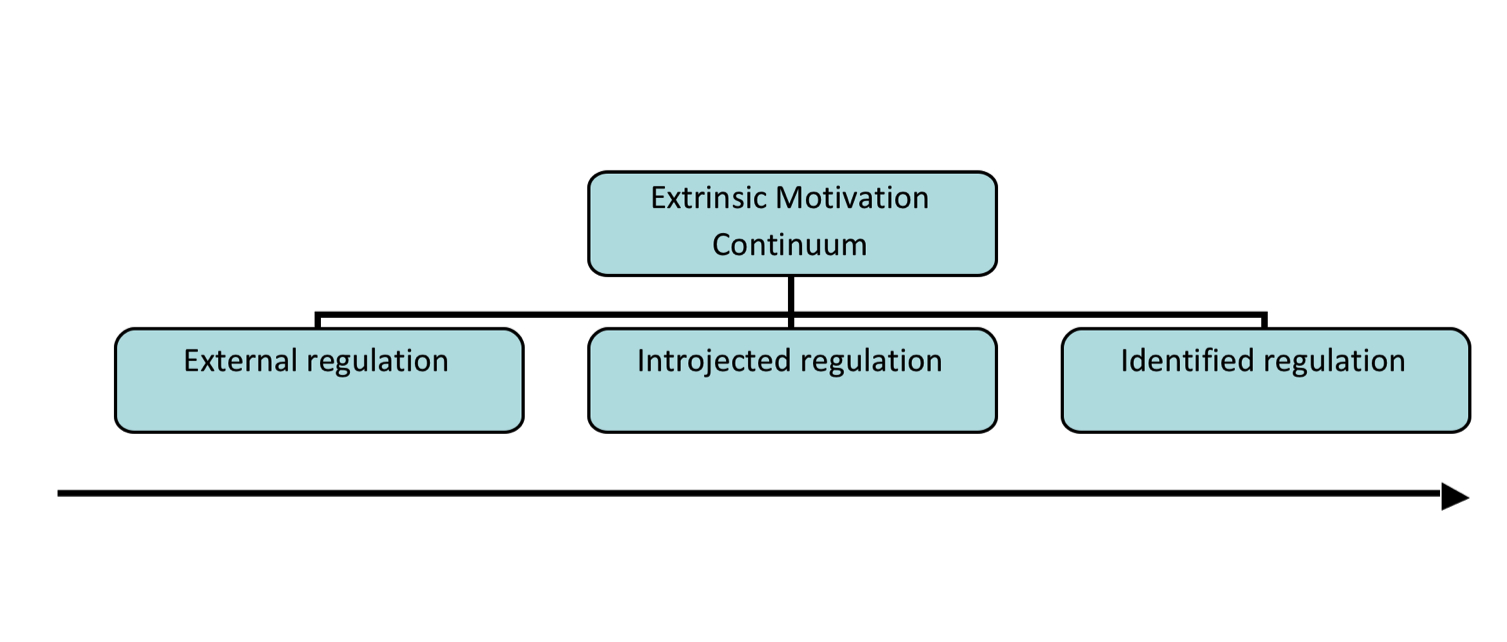
In order to sustain engagement for Deci and Ryan, motivation must be internalized . . . the external contingency must be “swallowed wholeâ€. By swallowed whole, the learner identifies the value of the new behavior with other values that are part of the self. This process of engagement is the transformation of an extrinsic motive, one that is reinforced from outside the learners’ values, into an activity that is assimilated and internalized by the learner as an intrinsic value that is part of their personal identity. This process involves constructing values aligned with the group and environment, and thus assimilates behavioral norms that were originally external as part of a new identity. Based on the degree of control exerted by external factors, levels of extrinsic motivation can be aligned along a continuum (Ryan & Deci, 2000).
- External regulation: doing something for the sake of achieving a reward or avoiding a punishment.
- Introjected regulation: partial internalization of extrinsic motives.
- Identified regulation: doing an activity because the individual identifies with the values and accepts it as his own.
Identified regulation is autonomous and not merely controlled by external factors. It is motivation for an activity that has been integrated as part of the learner’s values, and refers to identification with thvalues and meanings of the activity to the extent that it becomes fully internalized and autonomous (Ryan & Deci, 2000).
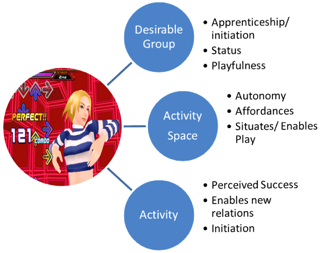
Themes for coding
| Play
Subjunctive Mood |
Activity Space | Desirable social grouping |
| Ritual Rites of Passage | Belonging/ Relatedness | |
| Desirable Activity | Identified regulation | Apprenticeship |
| Affective commitment | Autonomy/ Competence | Cognitive theories of action |
Eleven themes from these theories of identity construction, ritual/ rites of passage, engagement, motivation, and social learning were taken in order to code the interview transcript to inform analysis and make decisions on what factors might be important for the construction our afterschool program so that we can track design efficacy and measure performance.
Data collection
The phenomenological interview methodology (van Manon, 200*) was used to try and elicit responses beyond descriptions of rationale to gather “thick descriptions” (Geertz, 1973) of affective, social, corporeal, and cognitive behaviors (which the researcher hoped for but did not expect) behind the activity and experience of playing Dance Dance Revolution (DDR), but also to encourage descriptions that were thick enough that the researcher might be able to identify instances of engagement situated and distributed learning across networks of time and space, mediated through shared activity, Â and perhaps to see if there were evidence indicating whether identity construction and choice did inform motivation and engagement.
Data Analysis
The critical discourse methods as espoused by Gee (1999) and Fairclough (2003) not only provide methodologies that are fundamental to qualitative analysis, but are also fundamental to the study of “the scaffolding of human affiliation within cultures and social groups and institutions,†Gee (1999, pg 1) and “how do existing societies provide people with the possibilities and resources for rich and fulfilling lives,†Fairclough (2003, pg 202). It was for this reason that these methods were used to explore and code the phenomenological interview transcript. Although a sample of one participant is not very robust for generalization, it provided a starting point for more focused theory testing, as well as to provide insights for ourselves as designers, and education practitioners.
Interview
This first excerpt from the interview begins to describe the motivation to learn to play Dance Dance Revolution. Ellen and I met on a nice spring day in the Whittier neighborhood near the Minneapolis Institute of Arts at a coffee shop called Spy House. When I had asked her what was the experience of playing DDR, she said:
The first time I ever played Dance Dance Revolution was with my
friends Tyler and Ben. They had it at Devon’s house and everyone
was playing this game. Really, I wanted to hang out with them, I
wanted to participate and so that’s when I started learning. Then it
was after playing with those guys for so long that I really started to
enjoy the game. I actually didn’t have a play station before that, so
I went out and bought a play station just so I could play DDR, yeah. . .
yeah, I didn’t want to be left out of it. Games are fun and I just wanted
to spend time with my friends and this is something that they were
all doing.
The basis for Ellen’s learning was to Belong to a Desirable Group. This idea of relatedness and Belonging were fundamental in her development of skills and collection of resources to develop as a player. However, she did not have the feeling of connectedness until she was really able to engage in the activity as a participating member —Autonomy/Competence. Also of interest was that the activity was not initially a Desirable Activity, “I wanted to participate and so that’s when I started learning”. After some time participating, she found enjoyment along with her sense of Belonging to a Desirable Group. This phenomenon suggests precedence of Belonging to a Desirable Group over Desirable Activity, and also suggests that an individual can develop interest in activity that might not have been initially motivating. Speculatively, there may be some indication for the importance of play as a subjunctive for developing affinity for an activity. It was clear that she had already identified with the people, but, based on the next excerpt, she had not identified or been identified with the activity.
I was excited because this was something I could participate in. I’ve played Halo and I’m not that good at it and everyone was starting out on this for the first time, so I thought I could be one of those good people at it and get respect from people. I was really excited. They have this huge TV at Devon’s house and everyone’s around you. I was kind of nervous too because you have to do this in front of people. Well, we were all kind of sitting on the couch watching the men and I was like I want to try it. I mean, some of them were interested in seeing me probably because they knew I never played before and they made me where I was probably going to fail, but then I actually really wanted to do it, so I was like I want to do it next! I thought I was going to be better at the game than I thought I was because I’m thinking oh these guys they don’t have any coordination. This’ll be easy for me. I’m kind of in shape, so I was thinking it would be pretty easy and then I do some of these songs and I was like oh, I need to go down a level! I thought I caught on fairly quickly.
What was clear from this passage was the importance of the activity and her feeling that she could be successful participating and “be one of those good people at it and get respect from people.” There are several parts to this that are especially interesting:
- Belief in her ability to succeed was essential in her willingness to perform publicly. Research on adolescents’ engagement in literacy for example has found that adolescent perceptions of their competence and ability to succeed may be a more important predictor of whether they will engage than their past performance. (Alvermann, 2001; Anderman et al., 2001; Bean, 2000; Guthrie & Wigfield, 2000). Studies of adolescents have also found that they prefer to perform where they know they will have success (Csikzhentmihaly, 200*).
- The fear of performing in front of the group with Autonomy/ Competence but that since people were just starting out, she might have a chance to be good at it and to be respected. Thismay have played an even larger role because she was one of the girls who watch, not one of “the men†who play the games and perform.
- The importance of the Activity Space and its affordances as well as the possible change in atmosphere with this new game, where there may have been more emphasis on Play as the Subjunctive Mood.
This makes a case for the importance of Affective Commitment, Competence as well as a Cognitive Theory of Action. Although these seem to be sublevels of Desirable Activity and Belong to a Desirable Group, that inform and reinforce action. She had created a Cognitive Theory of Action and knew that it was essential for her to perform to be acknowledged and claim membership — another indication of Chapman’s (2006) description of engagement and evidence of Identifiable Regulation. To claim Belonging to this Desirable Social Group, she realized whether implicitly or not, that she needed to participate through performance (Autonomy/Competence) to Belong. This supports Deci and Ryan’s position that Autonomy, Belonging, and Competence are basic needs that underlie motivation and engagement and satisfy Skinner and Belmont’s assertion of affective involvement.
In addition, Ellen had already aligned her values internally as Identifiable Regulation— but she had not found an opportunity with a Desirable Activity where she might have success in the Activity Space where she could feel confident that she would succeed and enjoy the activity,
“I could be one of those good people at it and get respect from people”
Halo and Counterstrike she described as work (Sutton-Smith, 1996), which has consequences for failure — the desirable group may have been much more advanced in their performance in Halo and Counterstrike, and perhaps took playing the game much more seriously and raised the stakes of the performance.
Games and play are often about choices without life-threatening consequences, but that does not mean that games are not taken seriously. They can be performance tests (Autonomy/ Competence) and Ritual/Rites of Passage that allow for the development and affirmation of a place within a group, establishment of pecking orders, and through this, community status and entitlement . . . and it is possible that the experience of being positioned to perform and possibly fail was some sort of initiation, a form of deep play (Bentham in Geertz, 1975).
This act of bettering oneself in public is a tricky situation—but it really must occur in public for a person to be seen as Competent/Autonomous and an acknowledged group member (Belonging). This Ritualistic phenomenon was described by Geertz as the “Center Bet†in “Deep Playâ€, (1975) and based upon Ellen’s description, it may be that as play in an activity advances, the play gets more serious and the stakes and status of the Ritual change, and the work ethos takes precedence over Play as Subjunctive Mood.
In the DDR trial, Ellen was tested to see how she would respond to public failure: she could have quit and gone home, or she could laugh it off and find the fun in learning and work towards acceptance. As will be shown in the next excerpt, Ellen found that there were others who were beginners that she could get better with, and more experienced players were actually helpful and willing (Apprenticeship) to teach — she also found that there is no substitute for experience, and that in order to become a part of the group, she had to go through the rites of practice and public initiation–according to Van Gennep (1960) this ritualized process is common to many societies where an individual passes from one stage of life to another, and it can involve separation from childhood environment, transition, and incorporation with new status. For Turner (1969), this game may not be as monumental as rites celebrating marriage or death, but still represents a moment of social transition and eventual change in status. The importance of this is the public acknowledgement of Competence, and this seems to be essential to identity construction and acceptance as a member of a group (Buckingham, 2007).
The performance/ initiation
Previously, Ellen may have wanted to be part of the group, but Ellen stated that the games they were playing did not provide her with much interest to play, even though she wanted to belong with the group and participate in their space. Because of this, she may not have been considered as part of the group, but maybe more of a tourist or poser; because belonging seemed contingent on being able to “doâ€.
I have a lot of friends who play Counterstrike and a lot of . . . almost every guy I know plays Halo. You can enjoy watching those games. I don’t enjoy it as much. Like I said, it’s just way more serious. They get more serious. Well, it’s like everyone is more quiet and focused, like they really get into trying to hunt these people down and kill them before they are hunted down and killed. DDR, you are playing against someone but then with Halo and Counterstrike you’re against all these people and you have to be like watching your back all the time. Even the people watching, they zone out and just watch it. For me it’s not as fun. As for DDR, it’s more like people jumping around and are less serious but it’s still a lot of fun.
Prior to Ellen’s embrace of the game, she was a groupie. She could talk about how Devon did, but not about her own experience. This came in part as being recognized as a player by her community, but it was also a confidence that came of public performance (Autonomy/ Competence) and embrace of public performance; sustaining engagement with the practice; working hard to develop status and identity related to the group and the activity and the freedoms and responsibilities that accompany them.
So what followed was me just trying to find where I could go to play. Then I kind
of got eventually frustrated with it—well, not frustrated but I wanted to play more,
so I decided to buy it for myself.
Yeah.
You play by yourself to get better to play with other people. I mean, it’s always fun to play by yourself and unlock new songs and things like that.
I got it for Christmas from my parents, so I didn’t have to buy it but I had to persuade them and make sure they got me what I wanted. They didn’t really understand but they felt okay about it because it wasn’t something violent or anything like that.
Then I was like look what I can do! They watched me. They thought it was kind of interesting. This was with my family on Christmas. Then my uncles and my little cousin who was maybe like seven, they all got really interested by it. So my fifty-year-old uncles are trying it and they’re getting really excited. My little cousin, she’s getting excited too. She doesn’t even really understand what’s happening on the screen but she’s like jumping around on the pad.
The need for Activity Spaces should not be underestimated, but it seemed clear that Ellen was ready and willing to share her activity in a space, her parents’ holiday party to get the game system, mats, and software.
Ellen’s playing the game with family coincides with the Ritual of Integration/Aggregation as described by Van Gennep (1960), where Ellen has returned to her family with a new status. This status may not rival her accomplishments in sports, band or academics in her family’s values, but in many ways it was a revealing of how she had become different – how she had created difference and separated and returned, and her family’s embrace of this new part of her identity — “gamer girl”.
Dance Dance Revolution, and other games played in Devon’s basement provided an experience that offered the separation and initiation for obtaining group identity through the ritual of public performance that could be recognized not only by the group, but also by others away from the basement and through this the identity and status are further reinforced through the rite of integration. It was through the activity that Ellen was conferred status and identity as member not only by her new friends, but through her family and the community that had the power to convey her status and acceptance. This conferred new identity and acceptance allowed her to become that gamer beyond her normal relations and to extend her community network and be recognized by others to develop new relations and status:
because we shared this thing, so it would be like oh so who’s house are we going to go to tonight to play DDR? Okay. Well, my friend Devon, his house was the main DDR house just because he had a great room for it and everything and his parents didn’t really care how much noise we made or how late we stayed there, so his house is generally the DDR house. Tyler, who was my friend prior, we would get together                  and practice a lot. Michael, he bought DDR around the time that I did and we were basically kind of on the same level and I got to know him better that way just by spending time with all these people. Nick, all these other guys, I had kind of known beforehand but now we spent all this time together. So it was basically we all met at Devon’s house and that’s what we would do for weekend after weekend after           weekend.
If we can draw from these Activity Spaces and domains and inspire the learner to feel a connection and affinity to traditional academic fare like engineering, literature, mathematics, etc. What is also evident that we can create Desirable Activities that align with academic learning where the learning outcomes are embedded in the activity, that supports committed participation and engagement.
What makes Devon’s house a desirable Activity Space was probably the Autonomy they were given in the basement. Devon’s parents gave them access to a big television, let them come and go, let them choose their hours, and allowed them to express themselves with their music played loud in activities of their choice. This was probably trust earned versus parental apathy judging from Ellen and her friends, but this kind of Autonomy cannot be underestimated. What seems to make an Activity Space desirable is the ability to have Autonomy/ Competence, and perhaps this is one of the factors that make for a Desirable Group and the desire for Belonging/Relatedness as well as in creating a Desirable Activity.
Although there seemed to be many homes the kids could have had their gatherings, none of them seemed very prominent in her description, and the only mention Ellen made in the interview of Activity Spaces other than Devon’s were her parents’ house on holiday, when she was showing new friends how to play that were not part of her DDR group at Devon’s; when she would practice to ready herself for Devon’s; and the hotel room on her band trip to New York City.
As Ellen’s ability with the game progressed, she was being recognized as DDR “gamer girlâ€, and this conferred a new identity and status. She began to find new connections throughout her school experience, as more people knew about her new status as a “gamer girl” beyond her former status as an International Baccalaureate student (Academic), varsity soccer player (Jock/Athlete), Band Member (Musician). It may have been important for Ellen to branch out and change people’s perceptions In the same way that she described the Desirable Group:
“Really, I wanted to hang out with them . . . games are fun.”
and the proposition that might follow as if a syllogism, is that:
gamers are fun, and I want to be fun too.
Perhaps all that work in Academics, Sports, and Band had made her appear too serious, and maybe she felt constrained by all of her commitments and wanted to break out to meet new, fun people? It is only conjecture and anecdotal, and she did not abandon her commitment to band, sports, or academics — she did graduate with an IB diploma — but as can be imagined, all that work in those areas may have made it important to find friends who had interests beyond her everyday world, and that being with them would allow her to step away from conversations about the team, assignments, practicing to perform, and set her apart.
Developing these relations more than fun, but a coping tool. The importance of play, according to Vygotsky (1972), is decontextualization, where an individual can gain gratification and pleasure even in the midst of unresolved issues and larger, time consuming projects. The role of pretense and imagination can bring about pleasure and in the face of uncontrollable circumstances; this can provide some relief. Perhaps the gaming provided an opportunity to decompress and laugh in the midst of all that responsibility and preparation. An example of this may be seen in Ellen’s bringing the game on a band trip.
Yeah, it was a school band trip. So a lot of us went and it turned out that a whole bunch of people knew what DDR was. It was interesting to see them play. Tyler and I, we kind of felt cool because our group that we had played with had progressed better than these other people that we were seeing play. They were like oh man this kid is so good and we play with him all the time. Tyler and I played against these                people— Yeah, we beat them pretty bad.
In this instance, the game activity did extend beyond the familiar Activity Spaces like Devon’s basement; it even seemed to provide an activity that she could share with new groups as a Desirable Activity that would make others see her as part of a Desirable Group that others would seek Belonging/ Relatedness. The game seems to have supplanted the importance of being part of the gamer group in Devon’s basement, and the activity became a means for extending her friend network as Gee (2001) as an Affinity Group, where people affiliate because of an affinity for an activity. The next section demonstrates this. As the activity began to change for the group members, relationships started to change, and the emphasis on the game diminished.
Well, a lot of the guys that I started playing it with, they moved on to other games because that’s what they do. They focus in on something for a really long time and then they’ll find something else will be just released and everybody else will just be playing that, so they’ll jump into that. Then there was always the people who have it, like Tyler and I, who will still play it. We didn’t get bored with it; it’s just then there    were other things. No. I don’t play it as much as I do anymore and my friendships through that have become different. I mean, we’re all still friends. DDR was just like this common thing that we had to like start us talking and then after that we talked about normal things. I became pretty good friends with a lot of people. I dated one of  the guys that I met for awhile. I don’t know, it wasn’t like any different than like you      meet people playing for a sports team. You have something in common and that’s what you’re coming together to do, and then you talk about other stuff because we’re not just focused on DDR. Well, at my work it’s kind of similar too. We’re all stuck working together and so then we get talking. Soccer and sports a lot. Any kind of group that you all come together and you have something to talk about and then we  just eventually expand on that and that’s how we became friends.
The DDR game did facilitate the relationship in ways that other games and activities did not, but in the end, the initial motivation may need to come from purpose only the individual can formulate. But play can facilitate this and may make the entrance to a group, the practice, and eventual mastery of knowledge, activity space, and activity more likely to be enticing and possibly provide for sustained engagement and eventual mastery. This makes a case for Play as a Subjunctive Mood.
Playgroups, and the activities that support them, provide a common ground for interaction. There is definitely a pecking order that comes from demonstrable competence and evidence of knowledge from the semiotic domains from the game. Games are built upon play, pretense, and decontextualization, but once these activities no longer provide pleasure and gratification, the activity may quickly end and the relationships and spaces that contextualize and support them may change in the way that Ellen’s DDR group cooled off: “and my friendships though have become different. I mean, we’re all still friends.
Games are structured forms of play, Dubbels (2008) that provide rules and roles that are defined to help members to decontextualize from the ordinary world where they have responsibility, deadlines, and environments they cannot control. These same rules and roles also help them know their status in the game, share common, spontaneous, and authentic experience without going too deep into personal motives, negative feelings, and Freudian meltdowns. Corsaro (1985) called this play group phenomenon the Actors Dilemma, and according to Corsaro, the Freudian meltdown, or oversharing, is one of the most common causes of playgroup breakup—perhaps play is the coping mechanism that allows for detachment and the ability to constructively work on what can be changed and separating from that which cannot be. Game roles may also allows for exploration of other peoples’ values and experience in a safe space without getting too deep or real, which represents an opportunity to try on and project different emotions, and build comfort and trust through common experience.
In terms of Ritual/ Rites of Passage, a game would be a means for rite of passage, where the Activity Space is no longer like the ordinary world, and rules and roles are different and even changed for the sake of experimentation and normal social and interpersonal boundaries can be tested without endangering status and relationships. With Play as the Subjunctive Mood, different parts of person can emerge and people can try on different personae without recrimination — because they are only playing.
Conclusion
In answering the original question, “why did she sustain engagement?†it became evident that her motivation to sustain engagement over time changed. She was attracted to the activity because she wanted to be friends with the kids who hung out at Devon’s basement — she wanted to be an acknowledged member of the group, not part of the fan club. To do this she had to perform and risk ridicule and a possible reduction in status. Geertz (1976) described this spatially in that the further away you were from the Center Bet, where the desirable activity takes place, the lower your status and importance to the main event and performers.
In order to be part of this group, she needed to perform, but she might was hesitant to try because of the games they were playing did not mesh with her sense of play and fun—perhaps because the play of these group members with these games (Halo, Counterstrike) was already too far advanced for them to tolerate a “newb” (new player) at the controller; and it might be better not impose oneself and risk ridicule or contempt if one is not contributing to the play, learning, and or status of the group.
The role of Play as a Subjunctive Mood in these Activity Spaces and Desirable Groups may be the organizing principle that makes these groups and activities desirable as part of identity construction, as well as the means for identity construction. The subjunctive mood situates and mediates the discourse around the group desirability, the space and possibilities for interaction, and the perceived activity and likelihood for success and may be the basis for initial motivation to engage and represent the one constant throughout Ellen’s experience with the game, group, and space. For a person to facilitate and construct an identity, they may need to play, just as children play doctors, firefighters, teachers, mothers, and even animals in games. It is through pretense that we are able to imagine and create cognitive theories of action and circumstance and it is through play that we develop this capacity. If we want to sustain engagement, we need to help students develop the capacity for Identified Regulation, where they may turn their play into meaningful performance when asked to perform in activities that begin to resemble rites of initiation and deep play. This process creates a subtle transition where the initial play activity becomes serious and is approached with the focus of work, like what Ellen experienced watching advanced players of Halo and Counterstrike, and eventually what she experienced in practicing between school, homework, and lessons to prepare for DDR at Devon’s.
What was desirable about this Desirable Group? Probably their reputations as gamers and their ability to talk as insiders about what they were doing in an Activity Space where they were given Autonomy and Competence; it may have been their ability to create spontaneous neutral experiences that they could talk about in the grind of school-band-sports-work, and how they could look forward to this Ritual space away from the ordinary, where Play was the Subjunctive Mood and replicate this feeling in difficult circumstances to separate from stress and worry.
This ability to detach and decontextualize can be a very valuable trait when dealing with pressures of studying for exams, working, and other responsibilities that cannot offer immediate gratification. This inability to decontextualize and detach is one of the central behaviors inherent in Play Deprivation (Brown, 1999). The original diagnosis in the 1960’s in describing the incredible violence of Charles Whitmore and his shooting spree from the bell tower at Texas A& M University. It was found that Whitmore was raised in very rigid environment where he was not allowed friends or play. He experienced a life that looked very successful on the surface. But in 1966 he committed what was the largest mass matter in the history of the USA. According to the National Institute for Play website (last visited 4/9/09, http://nifplay.org/whitman.html), Brown, who was a psychiatrist at Baylor College of Medicine at the time, collected behavioral data for a team of expert researchers appointed by the Texas governor to understand what led to Whitmore’s mass murder. What was found through interview, diary, and reconstructing Whitmore
had been under extreme, unrelenting, stress. After many unsuccessful
efforts to resolve the stress, he ultimately succumbed to a sense of
powerlessness;Â he felt no option was left other than the homicidal-suicidal
. . . Whitman had been raised in a tyrannical, abusive household. From
birth through age 18, Whitman’s natural playfulness had been systematically
and dramatically suppressed by an overbearing father. A lifelong lack of play
deprived him of opportunities to view life with optimism, test alternatives, or
learn the social skills that, as part of spontaneous play, prepare individuals to
cope with life stress. The committee concluded that lack of play was a key
factor in Whitman’s homicidal actions – if he had experienced regular moments
of spontaneous play during his life, they believed he would have developed the skill,
flexibility, and strength to cope with the stressful situations without violence.
Brown continued exploring Play Deprivation as a construct and found similar patterns in other violent offenders, and even traffic deaths related to aggression and chemical issues. The role of play cannot be underestimated for its ability to decontextualize and reframe experience. Play therapy currently is a treatment in child psychology for helping children talk about and understand forces beyond their control.
Play may be vital to our well-being. It has been said that the opposite of play is depression, and depression can lead to feelings of powerlessness — the opposite of what we saw in Ellen’s attempt at Autonomy/ Competence and her efforts to connect. In this way, Play as a Subjunctive Mood may perform an important function in the ability to adapt, perform under stress, and create flexibility and adaptation for dealing with seemingly impossible situations — play may offer way out, a way to cope. But play demands time and space– especially spontaneous play – an activity, as was mentioned, where often we see young people working out issues they have no control over (as in play therapy).
It seems that all three of the social learning theories are context dependent based upon the needs of the individual at the time. Ellen, she was attracted to a Desirable Group as in Communities of Practice (Wenger, 1998) because of the activities and space where this group interacted. And there may have been factors that led to her admiration of these boys . . . it may have come from her admiration of how these kids conducted themselves at school and their reputations that they were fun “gamers”; but it was not until there was a Desirable Activity (Gee, 2001) that she could participate; and participation in a public performance was necessary for her to be acknowledged and feel Belonging/Relatedness (Deci & Ryan, 2008). As the group changed their focus on activity, the relationships changed, and new relations were created through the activity; but eventually the activity diminished and new activities and groups presented themselves as desirable.
The utility of this analysis comes from these recalled phenomena as a pattern for planning instruction and understanding why people learn. We learn to become. We create and engage to gain new experience and entitlement and gain status without danger in our social network, as well as to learn from others, whether it is a workplace competency, gaining social skills, or as a means of adapting to stress.
Implications / lessons for designing instructional environments
This transcript from Ellen’s experience makes a case for developing instructional environments that allow for playful, autonomous group interaction structured as a game to allow for play in much the same way that ritual demands play.
This process of making work playful, or working hard at play, is in some ways like finding a vocation or calling . . . in some sense the performance as ritual play, as described by Schechner (1994), is not far off when it comes to identity construction. Identity is bestowed through communal rites of passage, where individuals are sent away, learn, and perform, and then return to be recognized with a new identity and set of responsibilities. They are judged and identified based upon their performance. This idea seems especially appropriate for adolescents, who are in the process of identity construction, and are trying to find out who they are through trying out new activities, people, places, attitudes, identities, and things in society that has so many rituals and groups, but none communally organized that focus new identities and vocations.
There is distrust for activities that resemble rituals, games, and play. Part of this may stem from the independence required of play; the time involved in the rituals and competency development, and our general distrust of play as adult activity. Wohlwend (2007) looked at this notion of work and play through showing teachers video of children in classroom activity centers. Although there were clear examples of what was taken to be off-task behavior (Play), she found that teachers were able to find value in their students play if they were generative in creating connections and transfer to the students’ process and linking it to academic discourse.
The trouble with the perceptions of practitioners and policy makers seems to arise in the misperception between what Sutton-Smith (1997) called the Ethos of Work and Play. Given the opportunity, we may find that Play is a reasonable portal to motivation and sustained engagement through linking to the deeper learning that comes from identity construction and these oddly transformative communities that rise up out of them. In many ways, activities in formal and informal learning environments may not mesh with the intended identity of the learner, and this may indicate the difference between education and socialization along the lines of hegemony. The learner may choose a group affiliation antithetical to the purpose of the classroom.
So how might an educator integrate play, games, and lessons from these social learning theories?
I have used these principles on several occasions to explore games and play as effective methods for aligning content and process with resistant and reluctant learners.
Principle 1 — Play as a Subjunctive Mode
Engineering can be a very fun class, but the curriculum I was supposed to teach was very un-fun. In fact the curriculum was the source of the dysfunction. I was being asked to start class by presenting standards, why the standards were important, and tell the students why they were learning what they were learning. I found that this was much more for the benefit of observers evaluating the quality of my teaching than it was to motivate and engage the students.
I still use standards, and I still feel it is important to share the larger scheme of things behind activities and what they might be preparing for, but I do it with Play as the Subjunctive Mood. The first thing I did was to quit thinking these kids would commit to a curriculum where they were asked to redesign a coffee mug as an activity to learn engineering principles, fulfill standards and a rubric on a power point that came with the packaged curriculum. Fear of failure was not a big deal. Many of them were accustomed to it. They had checked out as an act of integrity and in doing so had found that they could dictate terms to teachers because of their disruptive behavior. Although my departure from redefining coffee mugs and the “do it or fail†curriculum did not sit well with the administrators, it did result in engagement from my students.
I told them that we were going to be having a boat race, and that I would be bringing in my wading pool from home, and that we would be making sail boats out of Styrofoam to race across the pool. I structured all of the engineering principles so that they were embodied in the task, and that through experience, we could discover them. What was essential in this case was not in joining a desirable group, but in participating in a desirable activity where their group could interact in the activity space semi-independently, and that the task was one where they believed that they would have early and instant success.
In addition to this, I also tried an experiment where I used a different approach to creation of subjunctive mood:
Work — I told the kids that we were really behind and that we would have to work hard and be rigorous in our approach to these boats. That it was incumbent upon us to learn terms like resistance, surface area, momentum, and force and apply them into our hull designs. What came from this my disappearance from their radar. I was talking, but they were ignoring me, tuning me out. When I asked them what they were supposed to do, many of them did not know, and many of them defaulted to resistant behavior.
Play — I told the class that we had a fun activity where we were going to be building boats and that we were going to have four kinds of races: speed, weight bearing, stability, and general purpose. I told them that I was going to be showing them examples of boat hulls and that they should play with them a bit to decide what style of boat they were going to make for the races they were going to participate in. I found that kids had listened, knew what to do, and really wanted to start. All of the same principles and terms were still present in the unit, but they now had permission to be playful and perhaps fail. Play implies failure recovery and experimentation. Many of the kids made crazy boats that would never work, but they were fairly successful in using the terms to justify their design for each race. It is not always what you do, or whom you do it with – it is how you do it.
Principle 2 — Desirable Groups
The role of Desirable Groups was primary for Ellen as a motivator for her becoming a DDR expert, but the tricky part about Desirable Groups was that underneath it was the issue of Play as Subjunctive Mood. A person may be attracted to a group for a number of reasons as we noticed from the three social learning theories. The grouping provides basic needs as in Self-Determination Theory; it provides apprenticeship and acknowledgement (Lave, 1998); and it may be ancillary, as in the attraction to participate with others in an activity. A Desirable Group can be a great motivator, but what was found was that eventually the Desirable Activity gets old and people move on and the group affiliation was not all that was necessary for sustaining engagement. This could be because the aspirant group member now understands what is behind Cool Kids Curtain Number One and the mystery of the cool kids is solved; or because the lesson from the apprenticeship has been assimilated. Whatever the motivation, indications were that she did join the group to learn who they were and why they were cool, and that after the fun with the activity wore out, the friendships drifted apart and they moved on to new activities. In addition, that the activity was used to branch out and connect with new groups.
With this in mind, we can situate and structure relations, change communication and status dynamics with Desirable Activities that are well-structured through Activity Spaces that have entitlement and opportunity. In thinking through some of the most well-constructed methods for creating cooperative groups, Cooperative Learning depends heavily on structuring Positive Interdependence (Deutsch, 1962, Johnson & Johnson, 1989) of the sort all three theories seek to describe, as well as construct through what was described from Play Group Literature (Corsaro, 19**) as spontaneous neutral experience, where people could build trust and common purpose.–where to succeed, everyone must succeed.(Johnson and Jonson, 2008, http://www.co-operation.org/pages/cl.html#interdependence).
The key element of groups seems to be status and what a person must do to get it. The danger of the Center Bet and the amount of support that comes with affiliation might be the deciding factor – Perceived Ability to Succeed—but it seems more likely that creating an atmosphere with Play as the Subjunctive Mood may be the best predictor of Group Desirability—which seems to come from status, space, activity, likelihood of success and acknowledgement.
Principle three — Spaces
Spaces are where we offer autonomy, equity, entitlement, objects, atmosphere, interaction, and relationships. By creating spaces where learners can self-govern to an extent, we make them desirable, especially if there are desirable tools and resources as affordances. What I did with the boat unit was to create a rite of passage to get from one learning space to another. An initiation where students had to perform to move to the next room — to make that desirable, I put the tools and materials there and gave the students (trustworthy students always get there first because they listen and finish the work early) and allowed them the autonomy to start and work with autonomy and privilege.
The students were told that in order to use the tools and start on their hull designs, that they had to use the hull examples and sketch a hull design In their engineering notebook, and then explain why and how the hull would perform well in specific race conditions (speed, weight-bearing, stability, general purpose) using the key vocabulary postered on the wall. When they were able to describe why and how their hull would perform well, they could go and begin building. This separation from one room to another was where I was able to coach, counsel, and cajole students into thinking more deeply about their designs, make suggestions, and enter their grades. All roads went through me as the Center Bet.
Principal four — Desirable Activities
One of the key issues in creating sustained engagement and identified regulation is in creating activities that align with the goals and purposes of the learner, or exposing the learner to something they think is really cool and they want to do. Making boats was not what many teens would consider a “cool” activity, but it did hold attraction for them when I showed them the tools, the materials, and gave a brief overview of what they would have to do. Getting kids to engage may just be a matter of creating some fun, and showing that they can have early and instant success; and, that they can make adjustments if they make mistakes. There must be time allowed to go deeply into learning to allow for the student to commit to expression in the work – the work has a part of them in it.
That will allow them to create a cognitive theory of the activity, and also allow for a belief in their future success. Add to this the opportunity to work cooperatively and learn from the work of other class members — some call this copying, I call it modeling and apprenticeship — then they can make a start (often full of errors and mistakes!) and adjust for excellence as they work with others and begin to better understand the project/activity. In this way we enable the spontaneous neutral experience that can be useful for beginning the learning process and also building relationships/ belonging, and autonomy and competence through the activity.
The key to this principle is in embedding the learning in the activity so that learners can discover the learning principles in the process of the activity through performance and reflection, where they compare what they have done with the work of others, and the instructor can provide encouragement to scaffold further development. Oddly, this is how scientific principles often presented in the textbooks were discovered before they were in the textbooks for memorization– they were tripped over by the scientists and then operationalized into methodology that some memorize as students, and others are lucky enough to rediscover in class. This can be done when we think of instruction as games and learning as structured forms of play. Some important elements for designing instruction as play are offered in this taxonomy of play for instructional design:
- Cognitive Theories of Action: we capture the imagination and build cognitive theories of action through imagery/ visualization (mental modeling).
- A key word for the instruction should be “IMAGINEâ€.
This first category in the taxonomy provides a basis for testing comprehension. It is important to be able to create mental model and theory of the action. The key attributes are visualization and imaginatively creating mental models and segmenting process and attributes for indexing in memory. If learners index and visualize well, they will likely have fine grain memory of the experience to draw upon for future use. So creating these mental images is very important for creating the motivation to engage, belief in future success, and a cognitive theory of action.
- Roles: provide roles and identities they can try on and play with, and offer the ability to change roles and play with the identities.
- A key word for instruction should be “IMITATEâ€
Working with others:Â A great draw because it allows for interaction. Many students need to be able to copy other students until they are able to IMAGINE and create a cognitive theory of action. Some learners do not learn well from instructors. They need to watch another learner translate the experience. Trough this, they not only learn how to start the assignment, but also how to create a cognitive theory of action on which they can improvise and express themselves through and commit to the activity. I cannot tell you how many times I have seen resistant learners get into a groove and not want to stop the project once they finally get started!
- Roles: In the case of the boat project, they became Naval Architects and Marine Engineers; just learning about what these folks do as a profession, and, that these professions exist opened a lot of high school eyes and creates schema for the semiotic domains of each role. They also had Learning and Functional roles – see Appendix B.
- Structuring group work: The creation of roles in cooperative learning as Johnson and Johnson suggest (200*) is very powerful and also what we see in early childhood play, as well as more advanced game experience for video games, teaching empathy, and modeling interaction for professional development. In structuring the work through roles, each group member has role specific tasks. Play Return to Castle Wolfenstein or look at game specific roles (character classes) in Appendix A, and imagine how these roles would culminate in teamwork for a mission. Each character class has several unique abilities and these come with different learning roles and functional roles.
- Rules — aka, the Identity Tool Box — Provide rules, values, language, actions, and tools associated with the roles and identities (semiotic domains) that they can work with and act upon that are inherent to the task, where the performance is the assessment. The role of the Naval Architect is to design a marine vessel for specific activities. The elements that define this role are the tools, activities, language, values, and outcomes associated with the role, and ultimately, the boat floats or it doesn’t. This embodiment is informative assessment, where the action provides immediate feedback through complete or partial mastery, or failure and the role provides for measure of progress and schema development based upon knowledge of the semiotic domains.
- Branching — Create choices and branching decision networks — and it is important here that the learners explain their cognitive theories of action and are asked to utilize and explain the identity tool box to support their choices and why they did what they did, and what might be next.
- Contingency/ Probability — this comes about when we consider the possible contingencies that might come from an action through prediction and hypothesis testing. Examples of this are resource management; awareness of likelihood of an action based upon knowledge of the game/ instructional environment, and attempted quantification and probability of failure/ success.
This structure for instructional design is a variation of A Taxonomy for Play from Dubbels (2008) and has been the basis for a number of successful curriculum units as well as digital games and is also available at www.vgalt.com.
A final note ~ Play as Subjunctive Mood
A brief experiment testing this occurred at Games Learning Society in a session called Real Time Research, where groups of participants from the RTR session went into the conference and conducted research on games. The author created a tool for measuring engagement to test whether Play as a Subjunctive Mood, or Work as a Subjunctive Mood would yield the greatest engagement from GLS conference participants. The hypothesis we were seeking to test was whether talk about play would elicit greater engagement on social, affective, and cognitive levels as compared to work.
The hypothesis was that people would engage with their descriptions differently when talking about work and play, and the sock puppet would elicit play behaviors and greater engagement. This would be gauged through analysis of the discourse captured in the video recordings of the interviews and then coded with a framework built from elements of engagement as summarized by Chapman (2003) and codified (see Appendix C).
The interviewees really engaged and took risks with the sock puppets. What is compelling about this experiment was that we were able to elicit more of the person with the sock puppet than we were with simple talk—there was much greater engagement and the participants seemed to enjoy the experience. The changes in treatments through creating different subjunctive mood –play versus work—were really quite dramatic.
What is important about these observations, as well as the finding of the analysis of Ellen’s experience with Dance Dance Revolution seems to be the expectations about interaction and purpose: Play as the Subjunctive Mood seems to represent a portal to engagement and its sustenance.
Appendix A
From the Wikipedia:
Soldier: The soldier is the only class that can use heavy weapons. They are: mortar, portable machine gun (MG42), flamethrower, and bazooka/Panzerfaust. On the No-Quarter mod the Venom machine-gun and the BAR (Allies) or StG44 (Axis) have been added as well. Leveling up gives the Soldier benefits such as the ability to run with heavy weapons (instead of being slowed down).
Medic: The medic has the unique ability to drop health packs, as well as revive fallen players with a syringe. They also regenerate health at a constant rate, and have a higher base health than any other class, which makes them the most common class for close-in combat. When a player has achieved skill level 4 in medic, they get Self Adrenaline, which enables them to sprint for, longer and take less damage for a certain amount of time. Some of the medics act as Rambo Medics. Their emphasis is on killing rather than healing or reviving.
Engineer: The engineer is the only class which comes equipped with pliers, which can be used to repair vehicles, to arm/defuse (dynamite or land mines), or to construct (command posts, machine-gun nests, and barriers). As most missions require some amount of construction and/or blowing up of the enemy’s construction to win the objective, and as defusing dynamite can be very useful, engineers are often invaluable, and one of the most commonly chosen classes. The engineer is also the only class capable of using rifle muzzle grenades.
Field ops: The field ops is a support class which has the ability to drop ammo packs for other players, as well as call air strikes (by throwing a colored smoke-grenade at the target) and artillery strikes (by looking through the binoculars and choosing where they want the artillery support fired). This class has low initial health, but makes up for having an unlimited supply of ammunition.
Covert ops: The covert ops is the only class which can use the scoped FG42 automatic rifle, the silenced Sten submachine gun (or MP-34 on some Mods), and a silenced, scoped rifle (M1 Garand for Allies, K43 Mauser for Axis). The covert ops has the ability to wear a fallen enemy soldier’s clothes to go about disguised, throw smoke-grenades to reduce visibility temporarily, and place and remotely detonate explosive satchels. By looking through a pair of binoculars, the covert ops can spot enemy landmines, bringing them up on their team-map. The covert ops also shows enemy soldiers on the team-map. Medic, Engineer,  This creates a fluid transition to the next category.
Appendix B
Functional Roles – Adopted from http://www.myread.org/organisation.htm (last visited 3/9/09)
ENCOURAGER and COP
- Reads instructions and directs participation
- Read the instructions
- Call for speakers
- Organize turn-taking
- Call for votes
- Count votes
- State agreed position
ENCOURAGER and SPY
- Summarizes findings and trades
ideas with other groups
- Check up on other groups
- Trade ideas with other groups
*Allowed to leave your place when directed by the teacher
ENCOURAGER and SCRIBE
- Writes and reports groups ideas;
is not a gatekeeper.
- Record all ideas
- Don’t block
- Seek clarification
ENCOURAGER and STORE KEEPER
Locates, collects and distributes resources including informational resources like web pages and encyclopedia entries
- Get all the materials for the entire group
- Collect worksheets from the teacher
- Sharpen pencils
- Tidy up
*Allowed to leave your place without teacher permission
LEARNING ROLE for LITERACY–
Freebody (1992) and Freebody and Luke (1990) identify the roles literate people take on.
CODE BREAKER
How do I crack this code?
· What words are interesting, difficult or tricky? How did you work them out?
· What words have unusual spelling?
· What words have the same sound or letter pattern or number of syllables?
· What words have the same base word or prefix or suffix?
· What words mean the same (synonyms)?
· What smaller word can you find in this word to help you work it out?
· What words are tricky to pronounce?
· How is this word used in this context?
· What different reading strategies did you use to decode this text?
· Are the pictures close ups, mid or long shots?
· Are the pictures high angle or low angle?
· Were there any word pictures, eg similes and metaphors? How did you work them out?
USER
What do I do with this text?
· What sort of text is this? (information, story/narrative) How do you know?
· Is it fact or opinion? How do you know?
· How can you find information in this text?
· How did the author start this text? Did it suit its purpose?
· Who would read a text like this? Why?
· If you wrote a text like this what words and phrases would you use?
· How is the language the same/ different from other similar texts you have read?
· Could the text help solve a real life problem?
· If you were going to put this text on a web page, how would it be different to the print version?
· What is the purpose of this text?
Could you use these ideas in a poem, story, play,
advertisement, report, brochure or poster?
· How would the language, structure and change?
PARTICIPANT (EXPERT)
What does this text mean to me?
· Does the text remind you of something that has happened to you or to someone else you know?
· What does the title/cover suggest that the text is about?
· What might happen next? What words or phrases give you this idea?
· What are the characters thinking and feeling? How do you know?
· What message is the author presenting?
· What are the main ideas presented?
· What do the pictures (graphs, diagrams, tables, captions, illustrations) tell us?
· Do they fit in with the text and do they provide more information?
· What did you feel as you read this part?
· Describe or draw a picture of a character, event or scene from the text.
ANALYST (INVESTIGATOR)
What does this text do to me?
· Is the text fair?
· What would the text be like if the main characters were girls rather than boys and vice versa?
Consider different race and cultural backgrounds too.
· How would the text be different if told from another point of view?
· How would the text be different if told in another time or place, eg 1900 or 2100?
· Why do you think the author chose this title?
· Think about why the author chose particular words and phrases.
· Are there stereotypes in the text?
· Who does the text favor or represent?
· Who does the text reject or silence?
· How does this text claim authority? (consider language, structure and content)
· Who is allowed to speak? Who is quoted?
Appendix C — Scoring for Play as Subjunctive Mood
Scoring categories for checklist:
A review of play research from Brown (http://nifplay.org/polar-husky.html, last visited 2/12/09) Informs this chekliostindicates that there are social cues that indicate play will be the subjunctive mood in an interaction.
SYM/ ASSM (Symmetrical/ Asymmetrical):
Symmetry indicates threat, standing ground, seriousness, and a willingness to confront and fight, whereas asymmetry indicates the willingness to play. The difference between SYM and ASSYM was the positioning of the body with eye contact, head positioning with arms, legs, chest, etc. ASSYM should be an indicator that the participant is in a play mood and interested in attachment/bonding.
ANIM/ NONANIM (Animated/ Non-Animated)
Play indicates an animated persona, where physical cues might include intentional clumsiness, excitement and affective energy, smiling, laughing. This links to affective involvement as well as cognitive theories of action.
POSTURE STIFF/ RELAXED
This is repetition of SYM/ASSYM, but represents a more general evaluation of body language regarding anxiety, fight or flight. This links to affective involvement as well as cognitive theories of action.
VOLUME VAR/CONSIST (Volume is varied / consistent)
This category indicates that the volume changes in tone, volume, and pitch. This variation indicates excitement and engagement, a commitment to playful behavior and task– as compared to monotone, where the person may be disengaged, depressed, or threatening. This links to affective involvement as well as cognitive theories of action.
EMPHASIS LESS/MORE
This category also refers to vocalization, where there are greater changes in emphasis in articulation–where words are shortened or lengthened for emphasis. This use of emphasis usually indicates more playfulness as compared to “measured emphasis” where words and elocution are carefully annunciated for the effect of seriousness. This links to affective involvement as well as cognitive theories of action.
COMPLEX VERBOSE/TERSE
This category also refers to vocalization, but is more focused on information than voice. The position is that a relaxed playful description will be more descriptive/ verbose. There will be more said in the explanation according Chapman (2006).
References
Alvermann, D. E., Moon, J. S., & Hagood, M. C. (1999). Popular culture in the classroom:
Teaching and researching critical media literacy. Newark, DE: International Reading Association.
Barit, L., Beekman, T., Bleeker, H., & Mulderij, K. (1983). Analyzing phenomenological
descriptions. Phenomenology + Pedagogy, 2 (1), pp. 1-17. Retrieved March 3, 2004, from http://www.phenomenologyonline.com/articles/barrit1.html.
Buckingham, D.(2008) Introducing Identity. In Youth, Identity, and Digital Media.The John D.
and Catherine T Macarthur Foundation Series on digital media and learning. MIT Press: Cambridge, MA.
Campbell, D.T. (1979) A Tribal Model of the Social System Vehicle Carrying Scientific
Knowledge. Science Communication.1979; 1: 181-201
Chick, G., & Barnett, L. A. (1995). Children’s play and adult leisure. In A. D. Pellegrini (Ed.),
The future of play theory: A multidisciplinary inquiry into the contributions of Bria Sutton-Smith, (pp. 45-69). Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
Corsaro, W. (1985) Friendship and peer culture in the early years. Norwood, NJ: Abex.
Csikszentmihaly, M. (1993) Talented Teenagers: The roots of success and failure. New York            Cambridge University Press.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience. New York: Harper & Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Row.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R.M. (2002) Handbook of Self-Determination Research. Rochester:
University of Rochester Press.
Deci, E. L. (1985). Intrinsic motivation and self-determination in human behavior. New York:
Plenum Press.
Dubbels, B.R. (in press) Video games, reading, and transmedial comprehension. In R. E. Ferdig
(Ed.), Handbook of research on effective electronic gaming in education. Information Science Reference.
Dubbels, B. (in press).  Students’ blogging about their video game experience.  In R. Beach, C.
Anson, L. Breuch, & T. Â Swiss, T. Â Engaging students in digital writing. Â Norwood, MA:
Christopher Gordon.
Eckert, P. (1989). Jocks & Burnouts: Social categories and identity in the high school. New
York: Teachers College Press.
Haase, M. (2002). Living with “obsessive Compulsive Disorder,†In M. van Manen (Ed.),
Writing in the dark. (p. 62-83). Althouse Press.
Holland, D. Lachiotte, W, Skinner, D. & Cain, C. (1998) Identity and Agency in Cultural
Worlds. First Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA
Freebody, P. (1992). A socio-cultural approach: Resourcing four roles as a literacy learner. In A. Watson & A. Badenhop (Eds.), Prevention of reading failure (pp. 48-60). Sydney: Ashton-Scholastic.
Back
Freebody, P., & Luke, A. (1990). Literacies programs: Debates and demands in cultural context. Prospect: Australian Journal of TESOL, 5(7), 7-16.
Gee, J. P. (1996). Social Linguistics and Literacies, Ideology in Discourses. Taylor & Francis.
Bristol: PA
Gee, J. P. (2005). Semiotic social spaces and affinity spaces: from The Age of Mythology to
today’s schools. In Barton, D. & Tusting, K. (Eds.) Beyond Communities of Practice. Cambridge University Press: New York, NY.
Gee, J. P. (2007). Good Video Games + Good Learning. Peter Lang Publishing. New
York: NY.
Geertz, C. (1973) Deep Play: Notes on a Balinese Cockfight. In The Interpretation of Cultures: Selected Essays. Basic Books. New York: NY.
Giorgi, A. (1997). The theory, practice and evaluation of the phenomenological method as
qualitative research procedure. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 28(2), 235-260.
Giorgi, A. & Giorgi, B. (2003). The descriptive phenomenological psychological method. In
P.M. Camic, J.E. Rhodes, & L. Yardley (Eds.), Qualitative research in psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Glickman, C. D. (1984). Play in public school settings: A philosophical question. In T. D.
Yawkey & A. D. Pellegrini (Eds.), Child’s play: Developmental and applied, (pp. 255-271). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Gramsci, A. (1971) Selections from the Prison Notebooks. International Publishers: New York,
NY
Greenblat, C. S. (1987). Designing games and simulations: An illustrated handbook. Newbury
Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Greenblat, C. S., & Duke, R. D. (1981). Principles and practices of gaming-simulation. Beverly
Hills: Sage Publications.
Heidegger, M. (1962). Being and time. (J. Macquarrie & E. Robinson, Trans.). San Francisco:
CA: Harper.
Huizinga, J. (1955) Homo Ludens: A study of the play element in culture. Boston: Beacon Press
Kafai, Y. (1994). Minds in play. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Lepper, M. R., & Chabay, R. W. (1985). Intrinsic motivation and instruction: Conflicting views
on the role of motivational processes in computer-based education. Educational Psychologist, 20(4), 217-230.
Lave, J. & Wenger E. (1991). Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Leander, k. & Sheehy, M.(2004) Spatializing literacy research and practice. Peter Lang
Publishing. New York. NY
Lewis, C., Enciso, P., Birr Moje, E. (2007). Reframing Sociocultural Research on Literacy:
Identity, Agency, and Power. Lawrence Earlbaum: Mahweh, NJ.
Loy, J. W., & Kenyon, G. S. (Eds.). (1981). Sport, culture and society: A reader on the sociology            of sport (2nd revised ed.). Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger.
Malone, T. (1981). Toward a theory of intrinsically motivating instruction. Cognitive Science,
5(4), 333-369.Malone, T. W., & Lepper, M. R. (1987). Making learning fun: A taxonomy of intrinsic motivations for learning. In R. E. Snow & M. J. Farr (Eds.), Aptitude, learning, and instruction, III: Conative and affective process analysis, (pp. 223-253). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Mayer, R. E. (1989). Models for understanding. Review of Educational Research, 59, 43-64.
McDermott, R. & Varenne, H. (1995) Culture as Disability. Anthropology and Education           Quarterly 26:323-348
Mumford, L. (1945) The Myth of the Machine: Technics and Human Development. New York:
Harcourt, Brace, & World.
Murray, J. (1997). Hamlet on the Holodeck: The Future of Narrative in Cyberspace. New York:
Free Press.
O’Brien, D.G. &  Dubbels, B. (Accepted) Promoting technological literacy. In Wood, K.E. &
Blanton, W.E. (Eds.) Promoting Literacy with Adolescent Learners: Research-based Instruction. Guilford Publications
Papert, S. (1993). The children’s machine: Rethinking school in the age of the computer.
New York: BasicBooks.
Pellegrini, A. D. (1994). The rough-and-tumble play of adolescent boys of differing
sociometric status. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 17, 525-540.
Pellegrini, A. D. (Ed.). (1995). The future of play theory: A multidisciplinary inquiry into the
contributions of Brian Sutton-Smith. Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
Pellegrini, A. D., & Smith, P. K. (1993). School recess: Implications for education and
development. Review of Educational Research, 63(1), 51-67.
Phillips, J. L. (1981). Piaget’s theory: A primer. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman.
Piaget, J. (1951). Play, dreams, and imitation in childhood. New York: W.W. Norton &
Company.
Piaget, J. (1952). The origins of intelligence in children. New York: BasicBooks.
Polkinghorne, D. (2003). Validation of qualitative knowledge claims. Published as Validation in
physical, organic, and human realms. In J. Linden & P. Szybek (Eds.), Validation of knowledge claims in human science (p. 11-24). Lyon: L’Interdisciplinaire.
Polkinghorne, D. (1989). Phenomenological research methods. In R. S. Valle & S. Halling
(Eds.). Existential-phenomenological perspectives in psychology: Exploring the breadth of human experience (pp. 41-60). New York: Plenum Press.
Rehm, M. (1990). Vocation as personal calling: a question for education. The Journal of
Educational Thought, 24, (2), 114-125
Salen, K. and Zimmerman, E. (2004).The Game Design Reader: A Rules of Play Anthology,
Cambridge: MIT Press
Sutton-Smith, B. (2003) Play as Parody of Emotional Vulnerability. In Play and Educational
Theory and Practice. Lytle, D. E. (Ed). Praeger: Westport. CT
Sutton-Smith, B. (1997) The Ambiguity of Play. Boston: Harvard University Press.
Tharp, R.G., & Gallimore, R. (1988). Rousing schools to life. “American Educator, 13″(2), 20-
25, 46-52.
Vallerand, Blais, Briere, and Pelletier (1989)
Van Manen (2002). Inquiry: guided existential reflection. Phenomenology Online. Last visited
6/20/2008. The World Wide Web: http://www.phenomenologyonline.com/inquiry/36.html
Van Manen, M. (2002). Writing in the dark: Phenomenological studies in interpretive inquiry.
London, Ontario, Canada: The Althouse Press.
Van Manen, M. (2001). Researching lived experience, (2nd ed.). London, Ontario, Canada: The
Althouse Press.
Vygotsky, L.S. (1978). “Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes”
(M. Cole, V. John-Steiner, S. Scribner, & E. Souberman, Eds. and Trans.). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Wenger, Etienne (1998), Communities of Practice: Learning, Meaning, and Identity.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Wohlwend, K. E. (2007). Reading to play and playing to read: A mediated discourse analysis of
early literacy apprenticeship. In D. W. Rowe, R. Jimenez, D. Compton, D. K. Dickinson, Y. Kim, K. M. Leander & V. Risko (Eds.), Fifty-sixth yearbook of the national reading conference (pp.377-393). Chicago, IL: National Reading Conference.

|

|
Developmental Changes in the Visual Span for ReadingMiYoung Kwon,a Gordon E. Legge,a and Brock R. Dubbelsb
a Department of Psychology, University of Minnesota, Elliott Hall, 75 East River Rd. Minneapolis, MN 55455 USA
b College of Education & Human Development, University of Minnesota, Burton Hall, 178 Pillsbury Dr., Minneapolis MN 55455 USA
Corresponding Author: MiYoung Kwon, 75 East River Rd, Minneapolis, MN, TEL: 612-296-6131; EMAIL:kwon0064@umn.edu
 The publisher’s final edited version of this article is available at Vision Res The publisher’s final edited version of this article is available at Vision Res See other articles in PMC that cite the published article. See other articles in PMC that cite the published article.Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
Children’s reading speed increases throughout the school years. According toCarver (1990), from grade 2 to college, the average reading rate increases about 14 standard-length words per minute1 each year. Learning to read involves becoming proficient in phonological, linguistic and perceptual components of reading (Aghababian, & Nazir, 2000). By age 7, normally sighted children reach nearly adult levels of visual acuity (Dowdeswell, Slater, Broomhall, & Tripp, 1995). By first grade, typically 6 years of age, most of them know the alphabet. Nevertheless, reading speed takes a long time to reach adult levels.
Many studies have addressed potential explanations for developmental changes in reading skills. Because it is often assumed that visual development is complete by the beginning of grade school, most studies have focused on the role of phonological or linguistic skills in learning to read (e.g., Adams, 1990; Goswami & Bryant, 1990;Muter, Hulme, Snowling, & Taylor, 1997). Consistent with this focus, one widely accepted view is that linguistic skills are predictive of reading performance and serve as the locus of differences in reading ability. According to this view, skilled and less skilled readers extract the same amount of visual information during the time course of an eye fixation, but skilled readers have more rapid access to letter name codes (e.g., Jackson & McClelland, 1979; Neuhaus, Foorman, Francis, & Carlson, 2001), make better use of linguistic structure to augment the visual information (Smith, 1971), or process the information more efficiently through a memory system (Morrison, Giordani, & Nagy, 1977) (as cited in Mason, 1980, p. 97). It is further argued that inefficient eye movement control observed in less skilled readers is a reflection of linguistic processing difficulty (Rayner, 1986, 1998) rather than a symptom of perceptual difference per se.
Stanovich and colleagues have critiqued the general view that differences in reading skill are primarily due to top-down linguistic influences. See Stanovich (2000, Ch. 3) for a review. Stanovich (2000) has summarized findings showing that recognition time for isolated words is highly correlated with individual differences in reading fluency. This work has focused interest on the speed of perceptual processing, rather than top-down cognitive or linguistic influences, in accounting for individual differences in normal reading performance. The differences in word-recognition time among normally sighted subjects could be due to differences in the transformation from visual to phonological representations of words, or to differences at an earlier, purely visual, level of representation. In short, it remains plausible that individual differences in reading skill, and also the development of reading skill, are at least partially due to differences in visual processing.
Five lines of evidence implicate vision as a factor influencing reading development. 1) The characteristics of children’s reading eye movements differ from those of adults, showing smaller and less precise saccades than adults (Kowler, & Martins, 1985). 2)Mason and Katz (1976) found that good and poor readers among 6th-grade children differed in their ability to identify the relative spatial position of letters. Farkas and Smothergill (1979) also found that performance on a position encoding task improved with grade level in children in 1st, 3rd and 5th grade. 3) It was found that children’s reading ability was associated with orientation errors in letter recognition such as confusing d and b, or p and q. stressing the role of visual-orthographic skill in reading (e.g., Davidson, 1934, 1935; Cairns, & Setward, 1970; Terepocki, Kruk, & Willows, 2002). 4) More direct evidence for the involvement of visual processing in children’s reading development was obtained by O’Brien, Mansfield and Legge (2005). They observed that the critical print size for reading decreases with increasing age. (Critical print size refers to the smallest print size at which fast, fluent reading is possible.) A similar character-size dependency of reading performance was also observed by Hughes and Wilkins (2000) and Cornelissen et al. (1991). 5) Letter recognition, a necessary component process in word recognition (e.g., Pelli, Farell, & Moore, 2003), is known to be degraded by interference from neighboring letters (Bouma, 1970). This crowding effect decreases with age in school-age children (Bondarko & Semenov, 2005) and is significantly worse in children with developmental dyslexia compared with normal readers (Spinelli, De Luca, Judica, & Zoccolotti, 2002). It should also be noted that there is a related debate in the literature over the role of visual factors in dyslexia, especially the impact of visual processing in the magnocellular pathway. For competing views, see the reviews by Stein and Walsh (1997) and Skottun (2000a; 2000b).
Collectively, the empirical findings briefly summarized above suggest a role for early visual processing in the development of reading skills. The question of whether there is an early perceptual locus for reading differences is an important one to resolve both for a better understanding of the reading process and for remediation purposes. In the present paper, we ask whether vision plays a role in explaining the known developmental changes in reading speed.
Legge, Mansfield and Chung (2001) studied the relationship between reading speed and letter recognition. They proposed that the size of the visual span2 – the range of letters, formatted as in text, that can be recognized reliably without moving the eyes – covaries with reading speed. They also proposed that shrinkage of the visual span may play an important role in explaining reduced reading speed in low vision. Work in our lab has shown that for adults with normal vision, manipulation of text contrast and print size (Legge, Cheung, Yu, Chung, Lee, & Owens, 2007), character spacing (Yu, Cheung, Legge, & Chung, 2007), and retinal eccentricity (Legge, et al., 2001) produce highly correlated changes in reading speed and the size of the visual span.Pelli, Tillman, Freeman, Su, Berger, and Majaj (in press) have recently shown that a similar concept, which they term “uncrowded span,†is directly linked to reading speed. The influential role of the size of the visual span in reading speed was also demonstrated in a computational model called “Mr. Chipsâ€, which uses the size of the visual span as a key parameter (Legge, Klitz, & Tjan, 1997; Legge, Hooven, Klitz, Mansfield, & Tjan, 2002). These empirical and theoretical findings provide growing evidence for a linkage between reading speed and the size of the visual span.
We measured the visual spans of children at three grade levels to examine developmental changes in early visual processing. The size of the visual span was measured using a trigram3 (random strings of three letters) identification task (Legge, et al., 2001). In this method, participants are asked to recognize letters in trigrams flashed briefly at varying letter positions left and right of the fixation point as shown in the top panel of Figure 1. Over a block of trials, a visual-span profile is built up – a plot of letter recognition accuracy (% correct) as a function of letter position left and right of fixation – as shown in the bottom panel of Figure 1. These profiles quantify the letter information available for reading. The method of measurement means that the profiles are largely unaffected by oculomotor factors and top-down contextual factors. Trigram identification captures two major properties of visual processing required for reading: letter identification and encoding of the relative positions of letters.
We distinguish between the concept of the visual span and the concept of the perceptual span (McConkie, & Rayner, 1975). Operationally, the perceptual span refers to the region of visual field that influences eye movements and fixation times in reading. The size of the perceptual span is typically measured using either the moving window technique (McConkie, & Rayner, 1975) or moving mask technique(Rayner, & Bertera, 1979). The perceptual span is estimated to extend about 15 characters to the right of fixation and four characters to the left of fixation. Rayner (1986) argued that the perceptual span reflects readers’ linguistic processing or overall cognitive processing rather than visual processing per se. On the other hand, the visual span is relatively immune to oculomotor and top-down contextual influences, and is likely to be primarily determined by the characteristics of front-end visual processing.
Rayner (1986) measured the size of the perceptual span and characteristics of saccades and fixation times in children in second, fourth and sixth grades, and in adults. He found an increase in the size of the perceptual span and a decrease in fixation times with age. These oculomotor changes could be due to maturation in eye movement control, or to secondary factors influencing eye movement control (either bottom-up visual factors, or top-down cognitive factors). Rayner (1986) attributed the developmental changes in eye movements to top-down cognitive factors because the size of the perceptual span and fixation duration were found to be dependent on the text difficulty. For example, he found that when children in fourth grade were given age appropriate text material, their fixation times and the size of the perceptual span became close to those of adults.
To confirm that oculomotor maturation is not the major source of developmental changes in reading speed, we tested our participants with two types of reading displays. First, Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP) reading minimizes the need for intra-word reading saccades, and removes the reader’s control of fixation times. Second, in our Flashcard method, participants read short blocks of text requiring normal reading eye movements. If maturation of eye-movement control is an important contributor to the development of reading speed, we would expect to observe a greater developmental effect in flashcard reading compared with RSVP reading. To the extent that growth in the size of the visual span is a contributor to the development of reading speed, we would expect to find a similar positive correlation with reading speed for both types of displays.
We also asked whether letter size affects the size of the visual span. Print size in children’s books is usually larger than for adult books. The typical print size for children’s books ranges from 5 to 10 mm in x-height, equivalent to 0.72 to 1.43 deg at a viewing distance of 40 cm (Hughes & Wilkins, 2002). Hughes and Wilkins (2000)found that the reading speed of children aged 5 to 7 years decreased as the text size decreased below this range while older children aged 8 to 11 years were less dependent on letter size. O’Brien et al. (2005) reported that the critical print size (CPS) decreases with increasing age in school-age children, showing that younger children need a larger print size in order to reach their maximum reading speed than older children. The critical print size (CPS) for adults is close to 0.2° (Legge, Pelli, Rubin & Schleske, 1985; Mansfield, Legge, & Bane, 1996). It has also been observed that the size of the visual span shows the same dependence on character size as reading speed (Legge, et al., 2007). It is possible that the use of larger print in children’s books reflects the need for larger print size to maximize reading speed. In this study, we used two letter sizes −0.25°, which is slightly above the CPS of adults and 1°, which is substantially larger than the CPS. Our goal was to assess the impact of this difference on the size of the visual span and reading speed for children.
We summarize the goals of this study as follows:
First, we hypothesize that developmental changes in the size of the visual span play a role in the developmental increase in reading speed. To test this hypothesis, we measured the size of the visual span and reading speed for children at three grade levels4 (3rd, 5th and 7th) and for young adults. A testable prediction of the hypothesis is that the visual span increases in size with age and is positively correlated with reading speed.
Secondary goals were to 1) examine the effect of letter size on the development of the visual span; and 2) to assess the influence of oculomotor control with a comparison of RSVP and flashcard reading.
2. METHODS
2.1. Participants
Groups of 10 children in 3rd, 5th, and 7th grade and 10 adults (college students) participated in this study. The children were recruited from the Minneapolis public schools. They were all screened to have normal vision and to be native English speakers. Students with reading disabilities, speech problems or cognitive deficits were excluded. Cooperating teachers at the schools were asked to select students in each grade level to approximately match students for IQ and academic standing across grade levels. Ten college students were recruited from the University of Minnesota with the same criteria. For each participant, visual acuity and reading acuity were assessed with the Lighthouse Near Acuity Test and MNREAD chart respectively. Proper refractive correction for the viewing distance was made. All participants were paid $10.00 per hour. Informed consent was obtained from parents or the legal guardian in addition to the assent of children in accordance with procedures approved by the internal review board of the University of Minnesota. The mean age, visual acuity, and gender ratio for participants in the different grades are provided in Table 1.
2.2. Stimuli
Trigrams, random strings of three letters, were used to measure visual-span profiles. Letters were drawn from the 26 lowercase letters of the English alphabet (repeats were possible). By chance some of the trigrams are three-letter English words (e.g. dog, fog) which might be easier to recognize. However, the chance of getting a word trigram is less than 2% which is not likely to have much influence on the overall letter recognition accuracy (c.f. Legge et al., 2001).
All letters were rendered in a lower case Courier bold font (Apple Mac) – a serif font with fixed width and normal spacing. The letters were dark on a white background (84 cd/m2) with a contrast of about 95%. Letter size is defined as the visual angle subtended by the font’s x-height. The x-height of 0.25° and 1° character size corresponded to 6 pixels and 24 pixels. The viewing distance for all testing was 40cm. The same font was used for measuring reading speeds (see below).
The stimuli were generated and controlled using Matlab (version 5.2.1) and Psychophysics Toolbox extensions (Brainard, 1997; Pelli, 1997). They were rendered on a SONY Trinitron color graphic display (model: GDM-FW900; refresh rate: 76 Hz; resolution: 1600×1024). The display was controlled by a Power Mac G4 computer (model: M8570).
Oral reading speed was measured with two methods–Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP) and a static text display (Flashcard). The pool of test material consisted of 187 sentences in the original MNREAD format developed for testing reading speed by Legge, Ross, Luebker and LaMay (1989). All the sentences were 56 characters in length. In the Flashcard presentation, the sentences were formatted into four lines of 14 characters (Fig. 2.b.).
The mean word length was 3.94 letters and 93% of the 1581 unique words occur in the 2000 most frequent words based on The Educator’s Word Frequency Guide(Zeno, Ivens, Millard, & Duvvuri, 1995). Mean difficulty of the sentences in the pool was 4.77 (Gunning’s Fog Index), and 1.34 (Flesh-Kincaid Index). According toCarver’s (1976) formula5, the mean difficulty level is below 2nd grade level. Allowing for differences in these metrics, the difficulty of the sentences is roughly 2nd to 4thgrade level. Sample sentences are presented in Figure 2.c. We divided the sentence pool into three sub-pools so that there were separate, non-overlapping sets of sentences for RSVP, Flashcard, and practice. Sentences were selected randomly without replacement, so that no subject saw the same sentence more than once during testing.
2.3. Measuring Visual-Span Profiles
Visual-span profiles were measured using a letter recognition task, as described in the Introduction. Trigrams were presented with their middle letter at 11 letter positions, including 0 (the letter position at fixation) and from 1 to 5 letter widths left and right of the 0 position. Trigram position was indexed by the middle letter of the trigram. For instance, a trigram abc at the position +3 had the b located in position 3 to the right of the 0 letter position, and a trigram at position −3 had its middle letter three letter positions to the left.
Each of the 11 trigram positions was tested 10 times, in a random order, within a block of 110 trials. The task of the participant was to report the three letters from left to right. A letter was scored as being identified correctly only if its order within the trigram was also correct. Feedback was not provided to the participants about whether or not their responses were correct.
Participants were instructed to fixate between two vertically separated fixation points (Fig. 1) on the computer screen during trials. Since there was no way of predicting on which side of fixation the trigram would appear, and the exposure time was too brief to permit useful eye movements, the participants understood that there was no advantage to deviate from the intended fixation. All participants had practice trials in the trigram test, RSVP test and Flashcard test prior to data collection. Participants were verbally encouraged to fixate carefully between the dots at the beginning of a trial.
Proportion correct recognition was measured at each of the letter slots and combined across the trigram trials in which the letter slot was occupied by the outer (the furthest letter from fixation), middle, or inner (the one closest to fixation) letter of a trigram. This means that although trigrams were centered at a given position only 10 times in a block, data from that position were based on 30 trials. As described in the Introduction, a visual span profile consists of percent correct letter recognition as a function of position left and right of fixation. These profiles are fit with “split Gaussiansâ€, that is, Gaussian curves that are characterized with amplitude (the peak value at letter position 0), and the left and right standard deviations (the breadth of the curve). These profiles usually peak at the midline and decline in the left and right visual fields. The profiles are often slightly broader on the right of the peak (Legge et al., 2001).
As described in the Introduction and illustrated in Figure 1 (i.e., the right vertical scale), percent correct letter recognition can be linearly transformed to information transmitted in bits. The information values range from 0 bits for chance accuracy of 3.8% correct (the probability of correctly guessing one of 26 letters) to 4.7 bits for 100% accuracy (Legge et al., 2001)6. The size of the visual span is quantified by summing across the information transmitted in each slot (similar to computing the area under the visual-span profile). Lower and narrower visual span profiles transmit fewer bits of information. In the Results, the size of the visual span will be quantified in units of bits of information transmitted.
Visual-span profiles were measured for each participant at two letter sizes (0.25° and 1°). In both cases, the stimulus exposure time was 100ms. The order of the two conditions was interleaved both within participants and across participants (e.g. participant A started with 1° letter size while participant B started with 0.25° letter size, and so on).
2.4. Measuring Reading Speed
Oral reading speed was measured with two testing methods: Rapid Serial Visual Presentation (RSVP) and static text (Flashcard method). For both testing conditions, the method of constant stimuli was used to present sentences at five exposure times in logarithmically spaced steps, spanning ~ 0.7 log units. For both reading speed tasks, the two letter size conditions were interleaved. The testing session was preceded by a practice session. During this session, the range of exposure times for each participant was chosen in order to make sure that at least 80% correct response (percent of words correct in a sentence) was obtained at the longest exposure time.
For RSVP, the sentences were presented sequentially one word at a time at the same screen location (i.e., the first letter of each word occurred at the same screen location). There was no blank frame (inter-stimulus interval) between words. Each sentence was preceded and followed by strings of x’s as shown in Figure 2.a. In the Flashcard reading test, an entire sentence was presented on the screen as shown inFigure 2.b.
For both tasks, participants initiated each trial by pressing a key. They were instructed to read the sentences aloud as quickly and accurately as possible. Participants were allowed to complete their verbal response at their own speed, not under time pressure. A word was scored as correct, even if given out of order, e.g., a correction at the end of a sentence, the number of words read correctly per sentence was recorded. Five sentences were tested for each exposure time and percent correct word recognition was computed at each exposure time.
Psychometric functions, percent correct versus log RSVP or log Flashcard exposure times, were created by fitting these data with cumulative Gaussian functions (Wichmann, & Hill, 2001a) as shown in Figure 3. The four panels represent four sets of data from RSVP and Flashcard tasks at two letter sizes. Five data points in each panel represent percent words correct in a sentence for RSVP and for Flashcard. The threshold exposure time, for words of a given length was based on the 80% correct point on the psychometric function. For example, in RSVP, if an exposure time of 200 msec per word yielded 80% correct, the reading rate was 5 words per second, equals to 300 wpm. For Flashcard, if the exposure time was 2 sec and the participant read 8 words correctly out of ten, the corresponding reading speed was 4 words per second, equals to 240 wpm.
3. RESULTS
Three dependent variables were measured: the size of the visual span, RSVP reading speed and flashcard reading speed. We conducted one ANOVA test for each measure. The grade level (3rd, 5th, 7th, and Adult) was treated as a categorical variable rather than numerical variable for the statistical analysis.
A 4 (grade) × 2 (letter size) repeated measures ANOVA with grade as a between-subject factor and letter size as a within-subject factor was tested on the size of the visual span. There was a significant main effect of grade level on the size of the visual span (F(3,36) = 9.54, p < 0.001). There was a significant interaction effect between grade level and letter size (F(3,36) = 3.46, p = 0.02). But no significant main effect of letter size on the size of the visual span was found.
A 4 (grade) × 2 (letter size) repeated measures ANOVA with grade as a between-subject factor and letter size as a within-subject factor was tested on RSVP and flashcard reading speeds separately. There was a main effect of grade level on RSVP reading speed (F(3, 36) = 7.80, p < 0.001) and Flashcard reading speed (F(3, 36) = 9.35, p < 0.001). No significant letter size effects on reading speed were found.
The effect of grade level on the size of the visual span and reading speed
The 4 × 2 repeated measure ANOVA test showed that there was a significant main effect of grade on the size of the visual span (η2 = 0.44, p < 0.01). A pairwise contrast test also showed that there were significant differences in the size of the visual span among all pairs of grades except between 3rd and 5th grades. The mean size of the visual span averaged across two letter sizes for the 10 participants is plotted for each grade in Figure 4. These results show that the visual span grows in size from 3rd grade (mean = 34.28 ± 1.17 bits) to adults (mean = 41.66 ± 0.87 bits). The effect size (using Cohen’s d) of the difference in the size of the visual span between 3rd grade and adults equals to 2.28.
We also found that there was a significant main effect of grade level on both RSVP (η2 = 0.39, p < 0.01) and Flashcard (η2 = 0.44, p < 0.01) reading speeds. Figure 5shows RSVP (left panel) and Flashcard (right panel) reading speeds (wpm) as a function of grade level. Open circles in both panels represent reading speeds for 1° letters, and the closed circles for 0.25° letters. Each data point represents the mean reading speed averaged across two letter sizes for a single participant.
As shown in Figure 5, there was a linear increase in both RSVP and flashcard reading speeds with grade level. As expected from prior research, RSVP reading speed was faster than Flashcard reading speed for all groups by an average factor of 1.58, which is fairly consistent with the results (i.e. a factor of 1.44) for a similar comparison by Yu et al. (2007). The growth in RSVP reading speed across grades exceeds the growth in flashcard reading speed, confirming the view that maturation of the oculomotor system is not a major factor associated with the growth in children’s reading speed.
The increment in flashcard reading speed per grade was consistent with earlier studies of page reading speed (Taylor, 1965; Carver, 1990; Tressoldi, Stella, & Faggella, 2001). Carver (1990) estimated that the growth in reading speed was 14 standard-length words per minute per grade level (where one standard-length word is equivalent to 6 characters). The average increment for Flashcard reading speed in our study was approximately 18 words per minute each year and its transformed value into Carver’s metric is 14 wpm, equal to Carver’s estimate.
Relationship between the size of the visual span and reading speed
Flashcard and RSVP reading speeds are plotted against the size of the visual span for our forty participants in Figures 6 and ​and77 respectively. The closed circles, open circles, closed squares, and open squares show data for 3rd, 5th, 7th grade, and adults respectively. The best-fitting lines for predicting reading speed from the size of the visual span are also shown.
There were significant correlations between the size of the visual span and Flashcard reading speed (r = 0.72, p < 0.01), and RSVP reading speed (r = 0.58, p = 0.01).
From the regression model for flashcard reading (Fig. 6), 52% of the variability of the reading speed can be accounted for by the size of the visual span (r2 = 0.52, p < 0.01). The slope of the regression line indicates that an increase in the size of the visual span by 1 bit brings about an increase in reading speed by 22 wpm. The effect size (Cohen’s d) is 2.29 for the difference in flashcard reading speed between 3rd graders and adults. Similarly, from the regression model for RSVP reading (Fig. 7), 33% of the variability of the reading speed can be accounted for by the size of the visual span (r2 = 0.34, p < 0.01). The slope of the regression line indicates that an increase in the size of the visual span by 1 bit brings about an increase in reading speed by 28 wpm. The effect size (Cohen’s d) is once again 2.29 for the difference in RSVP reading speed between 3rd graders and adults.
As described in the Methods section, reading speed was derived from the stimulus exposure time yielding 80% correct word recognition. To determine if the results were sensitive to this criterion, we reanalyzed the data with 70% and 90% criteria for defining reading speed. We found that the relationship between reading speed and the size of the visual span was not criterion dependent – correlations between size of the visual span and reading speed remained approximately the same across all three criteria (less than 0.01 differences in correlations).
The effects of letter size on the visual span and reading speed
We did not find a significant main effect of letter size on either the visual span or reading speeds in children. Contrary to the possibility raised in the Introduction, it does not appear that the use of larger print size in children’s books can be explained in terms of optimizing the size of the visual span.
While children in all three grade levels showed no dependence of letter size on the size of the visual span, adults showed slightly larger visual spans for 0.25° letters than for 1° letters (~ 3 bits). Legge et al. (2007) studied the effect of character size on the size of the visual span for a group of five young adults. They did not find a significant difference in the size of the visual span between 0.25° and 1°. We are unsure of the reason for the small discrepancy in the two studies.
4. DISCUSSION
Relationship between reading speed and the size of the visual span
It is obvious that visual processing is critical to print reading. It is not so obvious that individual differences in reading speed are linked to differences in visual processing nor that developmental changes in reading speed are influenced by visual factors. We have taken the theoretical position that front-end visual processing influences letter recognition which in turn influences reading speed. We have measured letter recognition in the form of visual-span profiles. The shape and size of these profiles are largely immune to top-down contextual factors and to oculomotor factors, and represent the bottom-up sensory information available to letter recognition and reading. The size of these profiles has been previously linked empirically and theoretically to reading speed (Legge, Mansfield & Chung, 2001;Â Legge et al., 2007). More specifically, it is hypothesized that the size of the visual span is an important determinant of reading speed.
As reviewed in the Introduction, it is known that children’s reading speed gradually increases throughout the school years (cf., Carver, 1990). The principal goal of our study was to determine whether visual development has an impact on this improvement in reading speed. We addressed this question by measuring changes in the size of the visual span across grade levels. Our hypothesis was that the size of the visual span would increase with grade level, and exhibit a correlation with reading speed.
These predictions were confirmed by our results. We found that there was a developmental growth in the size of the visual span from 3rd grade to adulthood paralleling growth in reading speed. A statistically significant 34% to 52% of the variance in reading speed could be accounted for by the size of the visual span.
Why does a larger visual span facilitate faster reading? For eye-movement mediated reading of lines of text on a page or screen (such as the flashcards in the present study), a larger visual span means that more letters can be recognized accurately on each fixation. With a larger visual span, longer words might be recognized on one fixation, or more letters of an adjacent word might be recognized if the fixated word is short (parafoveal preview). The effects of changing the size of the visual span were explored using an ideal-observer model, called Mr. Chips, by Legge, Klitz and Tjan (1997). Because a larger visual span means that more letters are recognized, the reader is able to make larger saccades; the greater mean saccade length facilitates faster reading. In the case of RSVP reading, there is no need for intra-word saccades or parafoveal preview of the leading letters of the next word. Only one word is visible at a time. In this case, we might speculate that the visual span need only be large enough to accommodate mean word length of the text (3.94 letters in the present study) or possibly the longest word in the text (8 letters in our text). If so, we might expect a weaker effect of visual-span size on RSVP reading speed, and possibly a ceiling once the visual span exceeded some critical value. These effects are not evident in the present data. Growth of the visual span manifests as both an increase in the breadth of visual-span profiles and also an increase in the height of the profiles, i.e., increasing letter-recognition accuracy in the central portion of the profile. The increased height of the profile could contribute to faster and more accurate recognition, even of relatively short strings. In other words, the graded form of the visual-span profile, and its potential growth in both height and breadth, can contribute to faster reading for both flashcard and RSVP text.
We recognize that our results are correlational in nature. It is possible that independent factors could drive the developmental changes in reading speed and size of the visual span. Although a causal link between the size of the visual span and reading speed remains to be proven, stronger evidence for a causal link has been provided by Legge, Cheung, Yu, Chung, Lee & Owens, 2007). These authors have amassed convergent data from several experiments on adults showing that the size of the visual span and reading speed vary in a highly correlated way in response to changes in stimulus parameters such as contrast and character size. For example, it is known that the dependence of reading speed on character size exhibits a nonmonotonic relationship in which reading speed has a maximum value for a range of intermediate character sizes, and decreases for larger and smaller character sizes. Legge et al. (2007) showed that the size of the visual span has the same nonmonotonic dependence on character size.
Sensory factors affecting the size of the visual span
What sensory factors might contribute to developmental changes in the size of the visual span? In the Introduction, we mentioned three candidate factors—errors in the relative position of letters in strings, orientation errors such as confusing b with d, and effects of crowding. We briefly comment on additional analyses of our visual-span data to address the roles of these factors.
Errors in relative spatial position (e.g., reporting bqx when the stimulus was qbx), sometimes termed mislocation errors, were evaluated by scoring trigram letter recognition in two ways; by demanding correct relative position for a letter to be correct, or by the more lenient criterion of scoring a letter correct if reported anywhere in the trigram string. The difference in percent correct by these two scoring methods is a measure of the rate of mislocation errors. An one-way ANOVA with grade (3rd, 5th, 7th, and Adult) as a between-subject factor revealed a significant main effect of grade on the rate of mislocation errors (F(3, 36) = 4.55, p < 0.01). The rate of mislocation errors increased with decreasing grade level (mean error rate for 3rd grade = 8.43 ± 1.1% and the mean error rate for adults = 4.25 ± 0.5%). Mislocation errors could be cognitive in origin, resulting from verbal-reporting mistakes, or visual in origin, resulting from imprecise coding of visual position. We think the latter is more likely because we found that the rate of mislocation errors was dependent on visual-field location, increasing at greater distances from fixation. This dependency of mislocation errors on letter position was consistent across all age groups.
We assessed orientation errors by measuring b and d confusions, and also p and qconfusions. Orientation errors are defined when b (or p) is reported instead of d (or p) and vice versa. The number of incorrect responses out of the total number of occurrence of b, p, d, and q is a measure of the rate of orientation errors. An one-way ANOVA with grade as a between-subject factor revealed a significant main effect of grade on the rate of orientation errors (F(3, 36) = 4.98, p < 0.01). Orientation errors decreased with increasing grade level (mean error rate for 3rd grade = 5.85 ± 0.40% vs. mean error rate for adults = 3.79 ± 0.38%). Since these children and adults would typically have no difficulty in distinguishing b from d, or p from q, in an untimed test of isolated letter recognition, we expect that these confusions result from the temporal demands of the trigram task or from adjacency of flanking letters (crowding) and have an impact on the size of the visual span.
In a separate preliminary report, based on this data set, we have shown that a decrease in crowding accounts for at least a portion of the growth in the size of visual span profiles across grade levels (Kwon & Legge, 2006). Pelli et al. (in press)have recently presented compelling theoretical and empirical arguments for the important role of crowding in limiting the size of the visual span (they use the term “uncrowded spanâ€), although they did not address developmental changes in the size of the visual span.
In short, relative position errors, orientation errors and crowding may all play a role in developmental changes in the size of the visual span.
Oculomotor factors
It is also possible that fixation errors could play a role in the observed developmental changes in the size of the visual span. Indeed, it has been reported that children’s fixation stability increases with age from 4 to 15 years (Ygge, et al, 2005). If children erroneously fixated leftward or rightward of the intended location in our trigram task, performance would on average, suffer; the mean distance of trigrams from the fixation point would increase as the size of the fixational error increases. We conducted a simulation analysis to evaluate the impact on the size of the visual span of such fixation errors. The key parameter of the model was the variability in fixation positions, represented by the standard deviation of an assumed Gaussian distribution of fixation locations centered on the correct fixation mark. An average adult visual span was used as an input parameter for each Bernoulli trial to obtain proportion correct for each letter position. Over trials, we computed the size of the visual span in bits of information transmitted. Through 100 repetitions, we obtained the estimates of the size of the visual span for a given fixation error. For example, if the standard deviation was two letter positions (σ = 2), 68% of the fixation points in the simulated trials would lie within ±2 letter positions from the intended fixation mark. As expected the greater the fixation errors (i.e., larger standard deviations), the smaller the size of the resulting visual spans. The simulation results indicated that fixation variability would need to increase from a standard deviation of 0 to more than 3 letter positions to simulate our observed reduction in visual span size from adults to 3rd graders. Moreover, fixation errors of 3 letter spaces for 1° letters would correspond to fixation errors of 12 letter spaces for 0.25° letters, producing devastating effects on the size of the visual span for the smaller print size. Because we did not observe print size effects on the size of the visual span, and because the fixation errors deduced from our simulation seem implausibly large, we doubt that fixation errors account for the developmental differences in the size of the visual span.
We also observed a substantial growth in reading speed across grades even in the RSVP reading where the need for eye movements is minimized. This result also confirms the view that developmental changes in reading speed can not be solely explained by maturation of oculomotor control.
Non-visual factors
Although we have focused on the size of the visual span as a possible factor influencing reading development, our data indicate that this factor accounts for at most 30 to 50% of the variance in reading speeds across grade levels. Non-visual cognitive and linguistic factors must also contribute to developmental changes in reading speed. It is possible that accidental correlations of one of these factors with grade level could masquerade as an effect of visual span. For example, if reading speed is correlated with IQ, and some unknown selection bias resulted in increasing mean IQ across grade level, then IQ might underlie the correlations we found between reading speed and visual span. In the case of IQ, this seems highly unlikely. Although we did not control for or measure the IQ of our subjects, we have no reason to suspect that there were increases in IQ across grade levels. Even if such a sampling bias exists, O’Brien et al. (2005) found no effect of IQ on maximum oral reading speed and critical print size in a group of children (aged 6 to 8) tested with MNREAD sentences similar to those used in the present study.
As another example, it is possible that children’s ability to recognize and speak the words used in our testing material varied across grade levels, accounting for the correlation between reading speed and grade level. For example, if children in the lower grades were unable to recognize and articulate words in the test material, even for unlimited viewing time, the missed words would count as errors in our scoring and result in reduced reading speed. We did not test word decoding skills of our subjects on a standardized test such as the subsets of the Woodcock-Johnson III Cognitive and Achievement Batteries (Woodcock, McGrew, & Mather, 2001). We did, however, screen all of our subjects with the MNREAD acuity chart (for a review of its properties, see Mansfiel & Legge, 2007). This chart, although designed as a test of the effect of visual factors on maximum reading speed, critical print size and reading acuity, uses simple declarative sentences with vocabulary consisting of the 2,000 most frequent words in 1st, 2nd, and 3rd grade text. The sentence material on the MNREAD chart is very similar to the test material in the present study. None of the words was missed or read incorrectly by our children for sentences above their critical print sizes. These observations lead us to conclude that untimed word-decoding skill was not a limiting factor influencing performance across grade levels in our study.
As yet another example of a potential non-visual influence, the oral reporting method used in the trigram task for measuring visual-span profiles might reflect more than the ability to extract visual information. Performance in this task could be influenced by articulation programming, rapid access to letter naming, memory capacity, and reporting accuracy. Many studies using rapid automatized letter naming (RAN) have shown that those component skills are highly correlated with reading performance (e.g., Denckla & Rudel, 1976; Wolf, 1991; Wolf, Bally, & Morris, 1986; Manis, Seidenberg, & Doi, 1999). It is possible that the underlying visual spans are actually stable across school age, but the observed changes in the size of visual-span profiles might be due to some later stages of processing. However, we think this is unlikely. In the trigram task, there was no time pressure to report the letters, so there were no requirements for rapid articulation and no time pressure on access to letter naming codes. It is still possible that younger children might make more phonological errors or transposition errors in reporting due to less efficient memory. Indeed, it is known that overall memory capacity including perceptual-memory improves with increasing age in children (Dempster, 1978; Shwantes, 1979; Ross-sheehy, Oakes, & Luck, 2003). However, convergent evidence has shown that children at the age of 9 are able to hold an average 5 to 6 digits or spatial symbols in their visual memory (e.g., Wilson, Scott, & Power, 1987; Miles, Morgan, Milne, & Morris, 1996). This result suggests that recalling and reporting a triplet of letters is not likely to pose difficulties for the children in our study. Manis et al. (1999) had 1st and 2nd grade students name 50 digits and letters in a random order aloud as rapidly as possible and measured reporting accuracy. They found that the rate of oral reporting errors was less than 2%, suggesting that by the end of first grade, most children know the names of all the letters and are able to report them with high accuracy.
These considerations encourage us to believe that the observed differences in the size of the visual span across age is likely to represent changes in the availability of bottom-up sensory information rather than effects of later stages of processing. Nevertheless, we cannot rule out the possibility that some other uncontrolled cognitive or other non-visual variable accounted for the apparent association between visual span and reading speed across grade levels in our study.
Effect of letter size
Finally, we addressed the effect of letter size. We expected that young children would have larger visual spans and read faster with 1° characters than with 0.25° characters. Contrary to our expectation, we found no effect of character size for either reading speed or visual span in children. Apparently, legibility as assessed by these two measures, does not account for the preference of children for larger print in books. It is possible that developmental changes in the effects of print size on reading speed are complete by 3rd grade (age 8–9 years), accounting for the absence of print size effects in our data. Consistent with this possibility, Wilkins and Hughes (2002) found that younger children aged below 7 showed a significant dependence of reading speed on letter size in the range 0.72 to 1.43 deg at a viewing distance of 40 cm, but older children above 8 years did not. Similarly, O’Brien et al. (2005) showed that critical print size (CPS) decreased with age from 6 to 8 years old, suggesting younger children need larger print to optimize reading performance. Taken together, it may be the case that the dependence of reading speed on print size becomes adult-like by about 8 years of age.
Summary
We summarize our conclusions as follows: 1) The visual span grows in size during the school years. 2) Consistent with the visual-span hypothesis this developmental change in the size of the visual span is significantly correlated with the developmental increase in reading speed. 3) Because both RSVP and flashcard reading speed increase with age, the growth in reading speed is unlikely to be due to oculomotor maturation. 4) We found no evidence that the use of larger print in children’s books reflects faster reading or larger visual spans for large print.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to students and teachers of the Minneapolis Public Schools for their participation in this study. We thank Beth O’Brien for her helpful advice on the earlier draft of this manuscript. We are also thankful to Sing-Hang Cheung for his help with the design of experiments. We would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by NIH grant R01 EY02934.
Footnotes
1Carver (1977) defined six characters in text (including spaces and punctuation) as one “standard-length word.†Measuring reading speed in standard-length words per minute is a character-based metric. Carver (1990) argued for the advantage of this metric over the common “words per minute†metric for measuring reading speed.
2The term ‘visual span’ was introduced by O’Regan (O’Regan, Levy-Schoen & Jacobs, 1983; O’Regan, 1990,1991). He defined the visual span as the region around the point of fixation within which characters of a given size can be resolved. Empirical studies have shown that normally sighted adults have a visual span of 7–11 letters. For a review, see Legge (2007, Ch. 3).
3Trigrams were used rather than isolated letters because of their closer approximation to English text. Text contains strings of letters. Most letter recognition in text involves characters flanked on the left, right or both sides.
4In this article, school grade levels refer to the American system. The correspondence between grade level and age is as follows: 1st grade (6–7 yrs), 2nd grade (7–8 yrs), 3rd grade (8–9 yrs), 4th grade (9–10 yrs), 5th grade (10–11 yrs), 6th grade (11–12 yrs), 7th grade (12–13 yrs), and 8th grade (13–14 yrs).
5We estimated the grade level from Carver (1976) who expressed the relationship between characters per word (cpw) and difficulty level (DL). According to his formula, the number of characters per word for 1st grade difficulty is approximately 5 cpw including a trailing space after each word, which is slightly above the number of characters per word (4.7 cpw) we used for our reading tasks.
6Percent correct letter recognition was converted to bits of information using letter-confusion matrices byBeckmann (1998).
This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
|
Teachers and teacher evaluation may be directly related to a construct from social psychology called Stereotype Threat and the relationship between motivation and teacher professional identities.
Stereotype Threat
Stereotype threat is the fear that we may confirm a negative stereotype about a group we belong to. From the wikipedia, we can read some of the history of the socio-cognitive construct:
In the early 1990s, Claude Steele, in collaboration with Joshua Aronson, performed the first experiments demonstrating that stereotype threat can undermine intellectual performance. . . Overall, findings suggest that stereotype threat may occur in any situation where an individual faces the potential of confirming a negative stereotype. For example, stereotype threat can negatively affect the performance of European Americans in athletic situations[11] as well as men who are being tested on their social sensitivity.[12] The experience of stereotype threat can shift depending on which group identity is salient to the situation. For example, Asian-American women are subject to a gender stereotype that expects them to be poor at mathematics, and a racial stereotype that expects them to do particularly well. Subjects from this group performed better on a math test when their racial identity was made salient; and worse when their gender identity was made salient.[13]

Certain individuals appear to be more likely to experience stereotype threat than others. Individuals who are highly identified with a particular domain appear to be more vulnerable to experiencing stereotype threat. Therefore, students who are highly identified with doing well in school may, ironically, be more likely to underperform when under stereotype threat. A key feature of this phenomena was highlighted by Amanda Schaefer at Slate Magazine. In order to counter stereotype threat, individuals need to experience positive development and build confidence over the course of a semester. Schaefer explains that a slightly better performance on test one leads to greater motivation and thus leads some individuals to work harder. That work then transcends to understanding of the material that then leads to greater confidence and even further motivation.
Teachers and Stereotype Threat
A recent study by the MeLife Foundation identified that teacher morale is at an all time low. This was discussed recently by the New York Times and a blog at Education Week. It would seem that teachers may be in a no-win situation. They are scrutinized for performance, often evaluated by administrators and others who may not be qualified to evaluate teacher performance. When faced with an evaluation, teachers may face serious professional and personal consequences when they do not satisfy criteria in the evaluation rubric, as interpreted by the evaluators. This was very nicely described in an opinion piece at the NY Times, called, Confessions of a Bad Teacher. In this article, the author writes:
I was confused. Earlier last year, this same assistant principal observed me and instructed me to prioritize improving my “assertive voice†in the classroom. But about a month later, my principal observed me and told me to focus entirely on lesson planning, since she had no concerns about my classroom management. A few weeks earlier, she had written on my behalf for a citywide award for “classroom excellence.†Was I really a bad teacher?
In my three years with the city schools, I’ve seen a teacher with 10 years of experience become convinced, after just a few observations, that he was a terrible teacher. A few months later, he quit teaching altogether. I collaborated with another teacher who sought psychiatric care for insomnia after a particularly intense round of observations. I myself transferred to a new school after being rated “unsatisfactory.â€
My belief is that if we are to avoid such things as stereotype threat in evaluating teachers, good administrators use the evaluation processes to support teachers and help them avoid those painful classroom moments — not to weed out the teachers who don’t produce good test scores or adhere to their pedagogical beliefs (Johnson, 2012).
The current culture of teacher quality and evaluation may be leading to issues in how teachers view their professional identities. They may be living two different professional lives–what they believe to work, and what they have to do to make the grade. This may be especially true with innovative teachers, who have to keep their heads down and teach in a way that works for them and leads to results. After I achieving, their  methods may be accepted. This comes from professional pride and ability. The question that must be asked is whether these innovators and creative teachers can document and demonstrate data-driven instruction.  This kind of instruction may not be applicable to generalized teacher quality assessments, because what the teacher is doing is not generally what is seen.  Is it possible an evaluator who is given a rubric is able or capable of making this evident after reviewing the teacher for  55 minutes they spent checking off cells on a rubric-driven evaluation?
 The Jekyll and Hyde Effect
The Jekyll and Hyde Effect
In the Jeckyll and Hyde Effect (Dubbels, 2009), teachers reported themselves in a situation where they had begun creating two different classrooms, two different sets of grade books, and two different teaching identities – culminating in the classroom they show, and the classroom they grow. These teachers had created a duality in professional identity, meaning that they had created different classrooms and identities to fit the expectations of the mandates, district mentors on learning walks, district trainings, and Professional Development Planning, so they could work “under the radar†and “not be hassled.â€
This phenomena seems to accompany most trends of educational reform.  In an article by Lasky (2005), it was posited that we may be destroying the professional identities of teachers by attacking their styles and beliefs about teaching and learning, and perhaps most importantly, their willingness to be vulnerable to reach kids and connect. Teachers expressed that they felt tension as professional educators, and that their beliefs about student learning often contrasted the current beliefs related to the culture of accountability.
According to Lasky (2005), this is not uncommon. In this passage (pg. 905) Lasky quotes and describes a veteran teacher considering leaving the profession because of frustration with “ladder climbersâ€:
Now there are lot of people who think this is a job to go to because the vacations are good, they follow the doctrines, and a lot of good people are leaving. The major message I was receiving was that you could make a difference, and we’re in this together, and it’s up to all of us to make the world a better place, you know, find your niche and dig in. And it was almost your job to do the peace and love thing. But the message now is that there’s no one to take care of you, you’ve got to watch your back, which is sad.
This teacher’s identity and sense of agency were in tension with the changing political landscape of reform. She found that she was not able to trust these people who were not willing to take the ‘‘real risks’’ entailed in teaching. One such risk is expressing one’s vulnerability;  such as knowing and standing up for one’s beliefs, connecting with students and doing all that can be done to help students from failing.
This can lead to a real hindrance in organizational and institutional trust, especially when it comes time for professional development activities that might require learning.  Teachers reported that they had seen “outcomes based education, constructivism, and profiles of learning†come and go. They reported that they had already invested a huge amount of time into these curricular approaches earlier in their careers, and were not willing to invest as heavily now that they had curriculum that worked for them. One teacher spoke of, “ I used to spend my weekends, afternoons, and evenings calling parents and correcting all for a .6 (part-time) placement, and I decided that I was working harder than the students and parents and not getting paid for it.†This teacher’s feeling was repeated throughout interviews with experienced teachers who shared that they had found an approach that they liked and allowed them to have lives outside of the classroom.
Identity and motivation
According to Dubbels (2009), formal learning seems to necessitate trust and identity. For Deci and Ryan (2002) the focus comes from work on motivation of basic psychological needs, with a focus on Autonomy — possibly built from early work by White (1959), where organisms have an innate need to experience competence and agency, and experience joy and pleasure with the new behaviors when they assert competence over the environment . . . what White called effectance motivation. If the individual gets social reinforcement and improved status in a relationship or community, they will be more likely be motivated to engage, and sustain that engagement, (Dubbels, 2009).
In order for a teacher to remain engaged in their profession and care about what is happening, and to sustain engagement , “motivation must be internalized†the teacher needs to identify the value of the behavior with other values that are part of themselves (Dubbels, 2009).  This internalization is recognized by others, and can be rewarded, ignored, or punished by the professional community, the students and parents, and administration and mentors for professional development. The same factors that we ask teachers to take into account for their classroom students are also at play in developing teacher professional development. This process of change includes public acknowledgement and awareness of making personal and professional change, and this public behavior can expose the individual to being vulnerable to the perceptions and judgment of others.
 The work I have done surrounding games has led to improvement in reading scores. In 2006-2007, I took over the Language Arts Instruction for an entire middle school in Minneapolis, MN. The students were primarily drawn from North Minneapolis, qualified for free and reduced lunch, and were very bright, but were not scoring well on the standardized assessments. I implemented a curriculum that studied video games as new forms of narrative. Games tell stories, just like the anthologies stacked on my shelves. The difference was that when I pulled out the anthologies, classroom management became more challenging, as most of the kids were willing to get a behavioral referral than sit through a reading of “The Treasure of Lemon Brown” from the anthology.
The work I have done surrounding games has led to improvement in reading scores. In 2006-2007, I took over the Language Arts Instruction for an entire middle school in Minneapolis, MN. The students were primarily drawn from North Minneapolis, qualified for free and reduced lunch, and were very bright, but were not scoring well on the standardized assessments. I implemented a curriculum that studied video games as new forms of narrative. Games tell stories, just like the anthologies stacked on my shelves. The difference was that when I pulled out the anthologies, classroom management became more challenging, as most of the kids were willing to get a behavioral referral than sit through a reading of “The Treasure of Lemon Brown” from the anthology.
These referrals were a lot of work, and there is no academic learning happening during that process.
I decided that instead of pushing stories at them, I should ask them what kind of media they liked. Most of them told me that they played video games and liked television, but few if any had any idea that there was anything of value in games besides entertainment. My role was to get them to understand literary elements, genre patterns, and critical thinking–the things being tested in the new standardized tests! The games provided an easy entry into narrative fiction, with the opportunity to also discuss genre and film techniques, as well as interaction and games studies.

Often people assume that kids are naturally good at games. That because they are young, that children are digital natives, and can comprehend and problem solves like secret genius in the wilds away from the classroom. Surprisingly, most kids are not fluent in how games work, they struggle with in-game problem solving, and they are often limited in discussing how games work. Surprised? One would have thought there would be an easy transfer of learning from games to books. But it was just not so.
There was no hidden genius here–many of the kids knew all about games, but few actually played them. Is this a digital native? When we use that term, we assume that these kids have great knowledge and critical thinking skills because of video games and television, and if we could only tap into them, they would show us the expertise we hoped was there with digital media, where they lacked with printed text. This was also found in a previous study.
Disappointing as that can be, games do offer a high interest, and more accessible narrative. I decided to use this opportunity to use their interest in games to develop their potential genius in books. Games provide interaction, social capital, and complex situations that kids can describe when taught to compose walkthroughs and multimedia book reports. The video games are actually were more accessible to kids: they have the same literary patterns, but the kids don’t have to take the step of decoding the words. This means we can practice literary elements with more accessible text. And I don’t mean infantilized “readability” accessible. I mean that the students were interacting with age appropriate, high interest, complex stories, and getting feedback as part of the game play. They could play and discuss, and build their awareness of the story, just like we do with reading circles.
The intent was to study games like we would study a printed text. Many of the students were game players, but few were very successful game players. This 9 week unit was well-received, as many of the students were interested in learning more about games, getting better at them, and doing something we did not ordinarily get to do in a classroom.
The difficulty that I was facing came from cultural beliefs about games. Many believe that games are devoid of learning and academic uses. This was especially true for many of my colleagues. They had the feeling that kids were just participating with weapons of mass distraction, and there would be a debt to pay on the upcoming state MCA2 reading test. For this reason, I made sure I educated my administrators, Milken TAP observers, and parents after I had done my planning. I made sue to invite stakeholders in to my room to observe, evaluate my instruction, and to interview kids and make them justify the unit by asking them direct questions about the value of studying games at school.
The kids did defend the unit, and made sure to back up what they were saying with examples. One student, Tony, when asked what value there was in studying Sonic the Hedghog replied, “you don’t understand, Sonic is just like the Odyssey story, he just wants to get home.”
Because a large percentage (38%) of my students were not even close to passing the Minnesota Basic Skills Test, I was questioned about the usefulness of this unit when I should be doing reading drill and practice. However, my administrators thought I had an innovative idea, and parents supported this unit.
So 38% of my eighth-graders had a cut score of 1 on the Minnesota Basic Skills Test (MBST) — a test based upon recall– and we were about to face the Minnesota Comprehension Assessment 2 (MCA2), which is a comprehension assessment based upon genre patterns and literary elements. The standards for reading and literature asked for the students to understand plot, setting, theme, etc. This is not a recall test.
My kids were all bright, but they had disengaged from the testing process, and the preparation for it. Saying something would be on the test was not motivating, but comparing a game title they looked to other texts we read was motivating. Now we were getting the practice necessary for identifying the kind of conceptual information necessary to do well on the MCA2: they began learning literary elements and genre patterns.
I created this curriculum of game study. The organizing principle was that games are new forms of narrative, and that by studying game narratives, I could teach them literary elements and genre patterns. I created rubrics and assignments from the literary elements from the Minnesota state standards and integrated ideas from traditional Language Arts curriculum.
This is what happened:
You will notice that between Seventh grade (Blue) and the Eighth grade the following year (Green) there was significant improvement. During that eighth grade year, we had better scores on a harder test. In a year when we switched from the Minnesota Basic Skills Test to the Minnesota Comprehension Assessment to the MCA2, we had significant improvement across the cut scores.
What you see in comparing my eighth-graders (GREEN–took the harder MCA2) with the eighth-graders the year before (RED — took the MBS) was that there was a significant difference in achievement differences in the bottom performers. There were significantly fewer in the bottom cut score: a 9% movement out of “Does Not Meet”.
When comparing tmy students 05-06 seventh-grade students their scores as eighth-graders, there was a 12% improvement.
Not only was there improved test performance, but I was seeing my students return to school, and showing improved performance in the classroom, and on the test. The return of these kids was very satisfying and I had fun teaching the unit. What was great was the change in the learning culture. The kids really valued the time we spent and professed that they were learning. But it was also satisfying to see an increase in the amount of students who met or exceeded the higher standard.
The unit was not easy, but the students had something interesting and more concrete to apply the concepts I want them to learn. Remember, I built my games unit on the standards. Games are another narrative. They have all the same literary elements and genre patterns. My students were basically doing a technical writing assignment in the form of a multimedia book report.
The bottom line, they surpassed expectations on the more difficult MCA2 test. We were expected to go down 12%. We went completely the other way.
We did do complementary readings, like The Odyssey, Raisin in the Sun, Sonny’s Blues, Langston Hughes, and more. The key element was that the kids now had a portal into these other areas. The video games unit gave them success, and showed them they could do it. A big part of this was the creation of meaningful rubrics, and my taking a role as facilitator rather than know-it-all. I could ask, I could use the language of the rubrics like roadmaps for assessments.
But the learning did not stop there. The kids opened to the learning,and the became willing to open the books. And I know it worked. We were taken on a field trip to the Guthrie Theater, and on our tour, we were taken under the stage. The docent told us that where we were under the stage was called “the underworld”. The kids ALL looked at me, and said, “is this why you brought us here? Just like in the Odyssey?”
I said, “of course, yeah!” not having any idea, and we laughed.
We had practiced using the abstract concepts like literary elements and genre patterns with more accessible narratives (games), and applied what we learned about game studies to talk about literature. We used game studies to leverage printed text. Stanovich calls this compensation–warming up cognitive cold spots with warm ones.
This unit valorized activities that kids choose and participate in outside of school. It created a situation where kids who were often not high achievers, but were smart and understood the games, could now take leadership, and use their prior knowledge and experience with games, and help classmates. This was a win-win for developing academic skills, and life skills.
Central to the student’s success was that the instruction and assessment were grounded with an empirical model of reading comprehension, which viewed comprehension as the construction of mental representation. The better kids are at creating mental representation, the better they will be at questions and problem solving.
Once students can visualize and create mental representation, the can reflect upon the story and begin to apply the literary concepts and genre patterns. This was easier with games because they did not have to learn from a text, and get to the content through decoding symbols into meaning. When they payed a game, they saw and experienced, and could conceptualize from what Piaget called Image Schemas–mental representations from the senses, and learn the characteristics of the literary terms in the context of the things they were abstracted from.
What many kids who struggle with reading face is not cognitive deficits, but a poverty of experience, and thus experience with the world to attach to the words and concepts we want them to learn. If you don’t know about music, reading about it will not give you a personal, or deep understanding. You may understand in theory, by learning one abstraction by connecting it to another–but this is wholly different than having experience to develop concepts through induction, rather than deduction.
But that is often what we do in the classroom. Present the abstract concept, and ask them to learn in by reading–another abstract process dependent upon decoding and translating symbols into mental images. This seems backwards. Imagine a child who has never seen a peach, or known anything about peaches trying to decode, “he lifted the peach to his mouth and was surprised to be tickled as he took a bite.”
Without prior knowledge and experience, the child cannot know about peach fur. Would you imagine arms and tickling fingers?
Games and objects ground instruction, and provide the basis for experience and mental representation — comprehension. When we have this, we can spend less time decoding and more time discussing printed text. So by writing about accessible narratives such as games, we were more successful when reading related printed text. We had learned process, concepts, and deconstructing problems. This led to huge changes in student academic performance and confidence.
The majority of my curriculum that year was in studying video games as new narratives.
Here is the curriculum
Here is a story about what we were doing
Here is a class you can take I have been offering for the last seven years. You can take it online here at Professional Learning Board.
There is a lot to learn in a game, but there is a whole lot more to learn outside of the game in documenting, listening, presenting ideas, and extending them, than just playing the games themselves.
If you want, there is a whole bunch of games curriculum on my teaching blog for language arts, reading, engineering, computer science, etc.
Everything from board games to curriculum for analysis of a time line. You might notice that they are set up to be run like a game.
I am hoping that this article makes a start for teachers embracing a model where they consider Learning by Design.Interestingly, games are also involved in assessment, and kids like to know their scores. The scores are an indication of learning.
And the learning is the fun part, the content and the problems are hard and learning is not always easy, but it can be desirable. Games are hard too, oddly enough, but when enough kids play them, and it creates enough buzz as social capital, there will be interest and some sacrifice to try and persevere in learning.
Tenacity, and metacognition are learned traits. With games and play, we can teach them.

What I like about what Katy did with this article is that she showed games in the classroom that do not have to pivot on the “digital natives” argument.
Kids like games, not all of them, but many kids are interested — it really does take a facilitator to motivate people and to create transfer to academic “work” or formal learning even if there is a high-interest activity available.
Teachers are important to practice and modeling to create a successful habit of learning the process of creating transfer.
That is, the kids need to learn how to learn, and think about learning.
This is called metacognition.
We all need to learn to question quality, question, raise and praise standards, be particular, and really think through the cognitive, social and cultural processes of comparison, combination, contrast, and reduction.
Learning by Design
The curriculum surrounding the games must be designed like a game in many ways:
- the directions are clear;
- everyone knows they can win;
- they can win in different ways;
- there are support and resources;
- there is clear criteria in the signal words for qualities and process.
What is the difference between learning with games and learning with text books?
Play as the learning mood (subjunctive mood) and therefore the social structures surrounding the games.
Also, kids have the ownership, and this puts the teacher in the role of facilitator who must be accepting of guiding the learner though the criteria–so if you have lousy criteria, and are not consistent with what your signal words mean in quality and process, expect lousy work, if not riots.
But if you put forward bad games, no curriculum or bad learning objectives, it is just like reading out of those boring collections of literature texts, without merit, and without no street cred.
The games are not the technology, the curriculum design surrounding the games are the technology. The computers only mediate good instructional design that teachers have always done in cooperative learning– and this exists in board games as well as it has in apprenticeship organizations to learn trades– just like it does in live action role plays, that in some genres, are what evolved into video games.
Good instruction is just good instruction. Hopefully this article takes folks towards that direction.
Because we can take the games and go a little further than merely connect.
Just playing a game may increase some cognitive functioning in low functioning people, but that does not mean that they can take that increase in in-game problem solving to in-life problem solving.
Being good at the game does not mean you will pass a reading test.
Does the reading test really matter?
Maybe not.
Should they be able to pass it?
Yes. They are not that hard.
The work I have done surrounding games has led to improvement in reading scores.
 You will notice that between Seventh grade (top-left) and the Eighth grade the following year (bottom-right) there was significant improvement in the school column. During that eighth grade year, I had all of the eighth -graders–but more importantly, we had a significant gain in a year when we switched from the Minnesota Basic Skills Test/ Minnesota Comprehension Assessment to the MCA2, which is a significantly harder test. What you see in comparing my eighth-graders with the year before was the movement from the bottom (who are the hardest to move btw) , the increase in students taking the test (they were all coming to class because of the curriculum), and the amount of students who met or exceeded a higher standard. I must admit, I built my games unit on the standards and my background in reading comprehension made games an easy connection — games are another narrative with all the same literary elements and genre patterns.
You will notice that between Seventh grade (top-left) and the Eighth grade the following year (bottom-right) there was significant improvement in the school column. During that eighth grade year, I had all of the eighth -graders–but more importantly, we had a significant gain in a year when we switched from the Minnesota Basic Skills Test/ Minnesota Comprehension Assessment to the MCA2, which is a significantly harder test. What you see in comparing my eighth-graders with the year before was the movement from the bottom (who are the hardest to move btw) , the increase in students taking the test (they were all coming to class because of the curriculum), and the amount of students who met or exceeded a higher standard. I must admit, I built my games unit on the standards and my background in reading comprehension made games an easy connection — games are another narrative with all the same literary elements and genre patterns.
The bottom line, they surpassed expectations. We were expected to go down 12%.
The majority of my curriculum that year was in studying video games as new narratives.
Here is the curriculum
Here is a story about what we were doing
Here is a class you can take I have been offering for the last seven years
There is a lot to learn in a game, but there is a whole lot more to learn outside of the game in documenting, listening, presenting ideas, and extending them, than just playing the games themselves.
If you want, there is a whole bunch of games curriculum on my teaching blog for language arts, reading, engineering, computer science, etc.
Everything from board games to curriculum for analysis of a time line. You might notice that they are set up to be run like a game.
I am hoping that this article makes a start for teachers embracing a model where they consider Learning by Design.Interestingly, games are also involved in assessment, and kids like to know their scores. The scores are an indication of learning.
And the learning is the fun part, the content and the problems are hard–and learning is not always easy, but it can be desirable. Games are hard too, oddly enough, but when enough kids play them, and it creates enough buzz as social capital, there will be interest and some sacrifice to try and persevere in learning.
Tenacity and metacognition are learned traits. With games and play, we can teach them.

Technology and Literacy
Current and Emerging Practices with Student 2.0 and Beyond
David G. O’Brien Brock Dubbels
Guiding Questions
- What technology tools and Web 2.0 applications are important for literacy learning
- What are the best practices involving technology and literacies
- How can instruction in the classroom and curriculum be enhanced by using new and evolving technologies that support digital literacy practices?
This chapter provides an overview of evolving research and theoretical frameworks on technologies and literacy, particularly digital technologies, with implications for adolescents’ literacy engagement. We suggest future directions for engaging students with technology and provide resources that support sound practices.
Evolving Research on Digital Technologies:
From Frameworks to Best Practice
When Kamil, Intrator, and Kim (2000) tackled a synthesis of research on technologies and literacy, they termed the task a conundrum. Given the rapidly evolving landscape of various technologies, that review, now dated (as this chapter soon will be), is still insightful both in reviewing a diversity of topics and the evolving importance of each. For example, at the turn of the decade, these researchers gave us historical footing in matters such as how computers and software may be used to improve reading and writing (Kamil, 1982), and to motivate learners (Hague & Mason, 1986). They noted the rising significance of hypertext and hypermedia, and foreshadowed the explosion of interest in the intersection of traditional literacies and digital media, which, at the turn of the decade, comprised a new program of inquiry (Reinking, McKenna, Labbo, & Kieffer, 1998). Finally, they also highlighted the social and collaborative importance of students working on stand-alone computers or in collaborative network environments, cited the paucity of research overall
on technologies and literacy, and expressed optimism about the future of computers as instructional tools.
In the same volume that featured the synthesis by as Kamil, Intrator, and Kim, Leu (2000) used the phrase “literacy as technological deixis†(p. 745) to refer to the constantly changing nature of literacy due to rapidly morphing technologies. Leu’s characterization is crucial, because he posits that these literacies are moving targets, evolving too rapidly to be adequately studied. If best practices rest on a solid research foundation, then, in the case of technologies and literacy we haven’t even begun to know what best practices are. Nevertheless, even in the midst of a shallow bed of “empirical†studies—that is, studies of specific effects, over time, with statistical power, or studies of carefully described and documented, contextualized practices—compelling frameworks have emerged, with implications for how technologies enable new literacy practices. Best practices, if based on solid frameworks rather than a carefully focused research program, can be extrapolated from the frameworks and be the basis for sound instruction and curriculum planning. In this chapter we bridge some of these frameworks with instructional practice.
The relatively brief evolution of technologies and literacy has led us from computers and software as self-contained instructional platforms to a networked virtual world that computers enable. In the past 10 years or so, we have moved from viewing the Web as primarily a source of information and as a sort of dynamic hypertext with increasingly sophisticated search engines, to Web 2.0. Albeit a fuzzy term that has accrued definitions ranging from simply a new attitude about the old Web to a host of perspectives about a completely new Web, Web 2.0 presents exciting possibilities for enhancing instruction and learning. This new Web is an open environment with virtual applications; it is more dependent on people than on hardware; it more participatory than a one-sided flow of information (e.g., blogging, wikis, social networks); it is more responsive to our needs (e.g., mapping a route to a previously unknown destination). Perhaps most important, Web 2.0 is more open to sharing of ideas, media, and even computer code (Miller, 2005). The presence of Web 2.0 is about the World Wide Web (WWW) as a platform for production. Software that users would normally purchase and install from a disk or download is now hosted on the Internet. In a sense, Web 2.0 affords anyone access to the largest stage yet conceived. Educationally, it has the potential to diminish the broadcast mode of information transmission that has reduced individual interests and engagement. Instead, learners can now have at their disposal studio-quality tools that enhance production, appreciation, recognition, and performance, and above all, provide access to a worldwide audience.
Whereas research on computers and reading and writing has remained sparse, research on the myriad literacy practices involved in the Web 2.0 phenomenon is sparse but growing rapidly and is informed by many theoretical frames and fields, most of which overlap—for example, multiliteracies (Cope & Kalantzis, 2000; New London Group, 1996), new literacies and new literacy studies (Coiro, Knobel, Lankshear, & Leu, 2008; Kist, 2005; Knobel & Lankshear, 2007), media studies and new media studies (Hobbs, 2007; Kress, 2003), and critical media literacy and popular culture (Alvermann, Moon, & Hagood, 1999; Beach & O’Brien, 2008), to name a few.
Each of these frameworks has its own dynamics for describing and studying literacy practices, and each is inextricably intertwined with other frameworks. In the rapidly emerging research base, most of the designs are highly contextualized and theoretically tantalizing, but few studies are gauged to identify specific generalizable practices. For example, the studies designed around some of the aforementioned frameworks vary in terms of methodology (spanning the full range of human and cognitive sciences); they vary in terms of which data are collected, which settings (physical and virtual) are studied, and how learners are defined (e.g., as information processors, real selves, virtual selves, identity constructors). Hence, we can present here only a small sampling and complement the descriptions with some “best practice†exemplars, reminding readers of the caveat that “research-based†practices represent glimpses or snapshots taken along the rapidly moving field.
Reader and Writer 2.0: New Literates and New Literacies
What is important about technologies and literacies, especially when considering adolescents? What should we cull from the myriad evolving frameworks and perspectives to be able to present something useful for teachers and learners at this point in time given this rapidly changing texture. First, we want to present the adolescent learner, the person we call Student 2.0, starting with a vignette.
High school students in Eden Prairie, Minnesota, a suburb of Minneapolis,posted photos on Facebook revealing themselves partying with alcohol, in violation of school rules. Following an investigation by school officials, disciplinary action was taken against 13 students. Students who believed that that the administration went too far walked out of school in protest; some of the parents threatened legal action (Xiong & Relerford, 2008). Scholars of digitally mediated popular culture challenged theadults, parents and school officials alike, to evaluate more critically what had happened: High school students felt a compelling need to express themselves as digital authors and document a relatively common practice, partying with alcohol. And issuing sanctions assumes that the practice had not been widespread before it was expressed publicly on Facebook. Prosecution of the rule offenders would only serve to remind the documentors to be more careful. The new media scholars also reminded the youth as authors to consider more carefully their audience in the future. When you post on Facebook, you create for everyone, including school administrators and parents. Some students who were interviewed on television reacted to the disciplinary measures by saying that their rights to free speech were violated, that the school administrators had no jurisdiction, because the activities happened off of school grounds. Others went back to Facebook to start a new group page to defend their actions.The Eden Prairie incident, albeit intriguing as a local interest piece about controversial legal and ethical issues regarding the Web 2.0, illustrates the trend of online content creation among youth. Rather than just use the Web to locate information, students are involved in content creation, that continues to grow, with 64% of online “teenagers†ages 12 to 17 engaging in at least one type of content creation, up from 57% of online teens in 2004 (Lenhart, Madden, Macgill, & Smith, 2007). In this national survey by the Pew Internet and American Life Project, 55% of online teens ages 12–17 say that they have
created a profile on a social networking site, such as Facebook or MySpace, and 47% of online teens claim to have uploaded photos where others can see them. Even though those students posting online photos sometimes restrict access, they expect feedback. Nearly 9 out of 10 teens who post photos online (89%) say that people comment on their postings at least some of the time. The number of teen bloggers nearly doubled from 2004 to 2006, with girls leading boys in blogging, and the younger, upcoming girls more likely to outblog The important issue for teachers is that these student authors are composing in a visual mode and reading comments printed in response; their peer readers (who are also most likely composers) are increasingly “reading†images and composing text responses or print messages in blogs and expecting critical responses. In short, students increasingly seem to engage in the
types of reading and writing they either don’t engage in, or don’t prefer, at school.
Experienced teachers can remember when stand-alone computers were going to revolutionize education; they can recall when the Internet was a cumbersome, text-based environment rather than an engaging graphical environment called the WWW. Those of us who, as literacy educators, have spent our careers studying how young people interact with printed texts are now faced with a new landscape that renders many of our theoretical models, instructional frameworks, and “best†practices based on these print models inadequate or even obsolete. Print text remains important but, as noted, expression is increasingly multimodal (Kress & Van Leeuwen, 2001). Reading and writing youth are increasingly likely to express ideas using different semiotic modes, including print, visual, and audio modes, and to create hybrid texts that defy typical associations between modes and what they traditionally represent.

When David worked with struggling readers in a high school Literacy Lab, the students, many of whom did not choose to read and write using print, wrote complex multimodal texts on a range of topics. They were very articulate about the affordances of various modes, and how those affordances influenced their choices in composition. For example, one group of students working a project exploring the impact of violence in the medion in adolescents, decided when to use images instead of print to communicate their ideas more effectively and passionately. They carefully planned how to juxtapose images and print to convey meaning. What would traditionally have been termed a “report†was instead a mul- timedia project, which they presented to parents and others at the school Open House evening. Brock has created a game studies unit, in which students study the qualities of their video games and create a technical document called a Walk- through using blogs, a wiki, video, and an animated slide show embedded into the blog. Students could read, compare, and evaluate other students’ work. Brock used an RSS feed (really simple syndication, a feed link to syndicated content) and had the blogs collected with bloglines, a way to both aggregate the student work and provide social networking through the WWW-based platforms and the comment sections for students.From these two examples, you can see that the reading and composition enabled by these digital technologies is spatial rather than linear. Linearity has been replaced by reading and writing in virtual textual space—where a hot link lures the reader away from one page and on to the next, and from print to images and video, deeper and deeper into one’s unique textual experience, and writers can post, broadcast, and receive responses. Scholars are already starting to look at the new spatial and temporal dimensions of digital literacies, as well as the compatibilities and incompatibilities of these dimensions
with traditional spatial and temporal dimensions of schools (Leander, 2007). Researchers are also studying new literacy environments such as web pages using research paradigms derived from reading print on paper—for example, Coiro and Dobler’s (2007) work extending traditional comprehension theories to study online reading comprehension. Coiro and Dobler argue that although we know a lot about the reading strategies that skilled readers use to understand print in linear formats, we know little about the proficiencies needed to comprehend text in “electronic†environments. McEneaney (2006) cogently argues that the traditional theoretical frameworks, including so-called “interactive theories†(from cognitive or transactional perspectives) are too strongly based in a traditional notion of print to be useful. With what are the new literates interacting? McEneaney contends that the text can “act on†the environment: The text can create the reader, just as the reader through the dynamics of online environments, can create or change the text.
But the new literates also encounter new challenges. The new textual spatiality lacks the kinesthetic texture of books; readers lose their “places†and even the ability to feel the touch of the page as they do when they flip paper pages back, then reorient themselves on the page (Evans & Po, 2007). The feel of the text is replaced by the feel of a finger on a mouse or a key. The imaging that helps a reader maintain and access the previous page might be replaced by multiple mental images of more rapidly changing texts, or mental images replaced by actual images. What Evans and Po call the fluidity of the digital or electronic texts invites readers to alter the text more readily, more easily. We come full circle with a tension faced by readers of the digital texts. On the one hand, this text fluidity begs readers to alter texts, to pick alternative texts, and to mix and match texts; on the other hand, this new textuality, with texts unfolding at every mouse click, places the text itself more in the control of the reader. The text the reader creates, often unwittingly via a series of clicks or cuts and pastes, may address the reader/writer in unexpected ways. One of the most exciting prospects for educators is the unlimited range of texts, from traditional print modes to various hybrids, including print texts, visual texts, audio texts, and even various types of performance texts that students can now create, as they themselves are “created†or changed by those texts. The new literates can navigate through a collage of print, images, videos, and sounds, choosing and juxtaposing modalities, and bending old spatial and temporal constraints to communicate to peers and to others throughout the world.
Beach and O’Brien (2008), in drawing from both the philosophy of mind and neuroscience (e.g., Clark, 2003; Restak, 2003) propose that the students of the “digital generation†have more digitally adept brains; they read and write differently than youth from even 10 years ago, because their existence
in the mediasphere, the barrage of multimodal information they encounter daily, the constant availability of multiple tech tools at their fingertips, and the convergence enabling immediate use and production of media have changed the way they process multimedially. Prensky (2001) has posited a similar scenario. The Beach and O’Brien proposal (2008), in response to a Kaiser Family Foundation study (Foehr, 2006) of young people ages 8–18 and widely disseminated in the popular press, shows that even though the total amount of time devoted to media use remains about the same as 5 years ago (6.5
hours a day), the amount of time devoted to multitasking, using multiple forms of media concurrently (e.g., surfing the Web while listening to an MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3 (MP3) and checking text messages), is on the rise. Beach and O’Brien (2008) contend that multitasking is not accurate, because it implies the ability to engage in several activities at the same time or, more accurately,to switch attention rapidly among activities to gain efficiency in completing work. They instead characterized this often seamless juggling as multimediating (Lankshear & Knobel, 2003), because it more accurately involves not only multimodal attention shifts but also seems to include a new facility and flexibility in processing and producing multimodal texts. The missing piece in characterizing the new literates is that we continue to appraise them using outdated models of reading, text processing, and learning. Instead, we need
to think of them as more adept at using technologies to read, compose, and “socialize.â€
Texts 2.0: From the Page to the Screen
Let us revisit the question posed in the last section—What is important about technologies and literacies?—and this time consider the evolving kinds of texts that youth are reading and writing. Again, we have to choose among compelling frameworks and perspectives. One salient issue surrounding the
evolving technologies is how the notion of “text†is changing. We are “moving from the page to the screen†(Kress, 2003). Kress notes that the screen privileges images. He also makes a case for the ambiguity of images and the necessity of print text for helping the viewer understand context and make a
directed interpretation of images. As educators, we have to concede that texts are increasingly multimodal (Jewitt & Kress, 2003). In multimodal reading and composing, ideas and concepts are represented with print texts, visual texts (photographs, video, animations), audio texts (music, audio narration, sound effects), and even dramatic or other artistic performances (drama, dance, spoken-word) (O’Brien & Scharber, 2008).
A second change is the increasing popularity of hybrid texts that are unlike most of the longer, connected discourse with which many of us grew up. For example, textoids are on the rise. These texts were originally defined as specially created research texts that lacked the coherence and structure of naturally occurring texts from typical genres (Graesser, Millis, & Zwaan, 1997) or contrived instructional texts (Pearson, 2004). Ironically, these once- contrived texts are ubiquitous in online environments. The term textoids now refers to fleeting texts that are transported from one place to another and are constantly changing (e.g., Wikipedia entries, pasted into a student’s report and edited to fit into the new textual context); they are also textual bursts of information sent to cell phones as text messages. Short textoids or text bursts are displacing longer discourse as readers expect more choices in accessing information and entertainment faster in quick clicks. At the same time, the sheer number and range of genres of these textoids, the juxtaposition of textoids with other media, and the retention of the more traditional, longer discourse, makes reading in online text environments more challenging than reading in traditional print environments.
The typical ways of describing and distinguishing texts from one another, such as using text structure, no longer apply (McEneaney, 2006). Electronic texts defy such classification, because they may be short and contrived to produce a targeted burst to get attention (the textoids); they are not linear but
spatial (hypertexts, hypermedia). Single textoids or pages or articles are linear, but they exist in virtual space, with a multitude of other possible texts. In short, the texts have virtual structure that is much more dynamic than static structures assigned to single print texts.
Present Technology Tools and Web 2.0 Applications
As we noted, Web 2.0 tools are about production, and they are hosted on the Web to enable a range of activities. As the access to bandwidth increases, and computers are equipped with greater image/video processing capacity, these tools will become invaluable in engaging youth. Young people will use these tools not only to develop literacy and numeracy skills but also to continue to hone their technological skills in the production, communication networking, data mining, and problem solving that are increasingly valued in the global economy. In the past, many of the tools now available as Web-based tools were expensive, limited to single machines, and difficult to use. These same tools, such as word processing, multimedia production, and network communications tools are now free, shareable, collaborative, and perceived as both meaningful and enjoyable by young people. Moreover, the tools are
part of young people’s daily lives. In addition, the personal electronics that many young people carry in their pockets, backpacks, and purses are more powerful than the computers that inhabited labs not even 5 years ago. With the advent of new applications and relatively cheap storage on the Web, these portable devices neither perform the bulk of processing nor store the outputs of processing; they are access devices—Web portals, with small screens and keyboards or other ways to input data. For example if you want to work with pictures, you can access a portal such as Flickr to view and manage pictures; if you want to create a document of just about any stripe, you can go to Google Docs and make slide shows; engage in word processing; construct spreadsheets; and store, share, and collaborate with writing partners.
Teachers can use many of these tools to extend and to enhance the learning experience of their students. The tools present challenges in developing best practices because they are neither repositories of content nor self- contained curricula. Rather, they can be used by creative teachers who are
able to draw from existing content domains, themes, and conceptual frameworks as they work within the applications; the tools can provide supportive environments for producing content, sharing and collaborating around content, and hosting public displays of users’ productions. Hence, the tools are not useful without the context of a larger unit or lesson plan, and instructional and learning frameworks that support activities and literate practices enabled by the tools. Teachers must understand clearly their instructional and learning objectives and goals, and students must know how the tools can help them meet those goals. Otherwise, the tools, which students sometimesknow well and can use for entertainment, revert to users’ tools for pleasure and interests, easily circumventing instructional or learning practices desired by teachers. Next, we review some Web 2.0 tools that enable these practices, and describe the features of each, presenting examples of how we have used them with students.
MySpace
We start with the nemesis of most computer classrooms and labs. For example, Brock was observing another teacher’s students during a drafting class. The students were working in a lab with high-end three-dimensional drafting software. During downtime between instructions that were broadcast over the
public address system, students often checked their MySpace pages. Although the site was blocked in the district, many students easily overcame the obstacle by searching for a proxy server that granted them access. A proxy server is a website that has a name accepted by the firewall, so it is allowed—it is kind of like using a fake ID. Although students may not know how it works, they have learned how to do it. And no matter how savvy the information technology (IT) department, the almost infinite supply of new proxy servers and webpages, with directions targeting youth who want to jump the school restrictions, makes sites deemed objectionable by school districts difficult to block.
On the one hand, to the digital immigrants and the inhabitants of the Institution of Old Learning (O’Brien & Bauer, 2005), MySpace represents an uncontrolled virtual space that distracts students from work and enables socializing and forms of expression incompatible with the organization and temporal control of school. On the other hand, for digital natives, “assimilated†digital immigrants, and new literacies advocates, MySpace is a dynamic forum of multimodal expression. It is also a place where young people socialize with peers around the world, put pictures up, write in slang, stream music and video, and engage in instant messaging. They are able to blog, to embed flash animations—in short, to engage in almost limitless expression using a range of multimodal literacies. It is really an example of students expressing themselves in the same way they dress, decorate their rooms, or draw in their notebooks.
This does not mean that the space is benign. Although you can connect with friends and family, you can also get solicitations from unwanted characters. Most young people are aware of whom to talk to, and how they expect others to speak to them. Users know that others mask their true identities through the computer, which has led young people to be more savvy as well. The Kaiser Family Foundation Generation M report (Roberts, Rideout, & Foehr, 2005) notes that when kids come across inappropriate sites and solicitations, they move past them. For digital natives, experienced in social networking, these are just another distraction in the way of what they went to the site to do. MySpace sites can also be locked to persons other than those invited by the owner.
We don’t expect sites like MySpace to be imported into the school curriculum. However, in the spirit of being more assimilated into Generation M’s world, it makes sense for teachers to join MySpace, set up a page, and even let students know that you have done so. As teachers, we interact regularly with our students via MySpace. Through it, we are more in tune with their social worlds, their interests, and their creativity. You might also want to bridge media production in school with the sharing features of such social networking sites, so that students may use tools like MySpace as a way to share and to get feedback on their productions.
You already know a bit about Facebook from the Eden Prairie vignette. It is a place where you can post your profile and surround yourself with friends, their activities (including photos of parties!) and favorite sites, and connect the dots to all of your websites. Brock has links to SlideShare, mogulus television station, Facebook social networking groups, and various blogs. Facebook also includes tons of little games, multiple ways you can communicate with others, and things you can share. Brock is a member of many groups, and when the mood catches him, he starts another group: How about people who have read this chapter and want to continue the discussion about literacies involved in applications for Student 2.0? It really is that easy, and he really did start that group.
In Facebook you can choose to keep up with friends you don’t see often, as well as friends and acquaintances with similar interests and affinities. You can take surveys of movies and compare them to your friends; you can see what kind of German or French philosopher you are. You can share music,
keep up to date with friends through instant messaging, and be alerted to activities of groups to which you belong. Facebook, like MySpace, is blocked in many school districts, although most of adolescents we know seem to prefer MySpace. As with MySpace, we encourage teachers to set up a Facebook account to see what it provides. Although it might be tricky if the site is officially blocked in school, we also encourage teachers to use it to network with both colleagues and students. One of the great revelations, if you are included as a “friend†to students classified as “struggling†in reading and writing, is the quality, the range of genres, and the passion with which these students compose and engage in reading others’ compositions on social networking sites. It is possible that these same students, who have negative perceptions about their abilities and avoid reading and writing in school, might invite teachers to read what they have written online.
YouTube
Unfortunately, YouTube is much maligned in schools, not just because of the content, but also because streaming media consume bandwidth. This is the most complete compendium of online searchable video ever. Like any compendium, including the billions of webpages outer there, there are some videos
that teachers may find either objectionable or a waste of time, just as there are thousands of interesting and informative videos. There are really many opportunities for using Web-based video in the classroom. Here are several ways that we have used it:
1. To show a video.
2. To host a video we have produced.
3. To engage in social networking.
4. To enhance engagement among students.
5. To provide content for a Web-based, TV-like network with Mogulus. Â Â (now Livestream)
The real value of video is its impact due to availability of narrative, and the power of performing and presenting to the world—something that local and even national networks cannot do. YouTube not only hosts videos created by your students but also provides access to videos created by novices and professionals from all over the world. YouTube should be a part of classroom instruction designed to teach appropriate use of media and media savvy to young people. With YouTube you can embed video in your blog and your website, as well as upload your own creations—even from your cellular phone. We have observed that when students create for performance and presentation to an audience other than their teachers and immediate peers, they put forth much more effort and are much more creative and engaged, and the learning experience lasts long after the week-and-a-half extinction point of most test- driven curricula. Students can create, post, and share. In addition, teachers can create groups and utilize social networking to perform and to respond. The most powerful benefit is that this social networking and broadcasting function extends and deepens the possibility of participating in high-traffic media networks, where millions of people may view your work and send out links to invite their friends to see what you have done. With the right topic and a bit of luck, a cell phone with video capture and a good idea can start a person’s career in video media. This prospect can be motivating, and the idea that students have done something that everyone can see leads them to some real street “media cred.â€
Flickr
This photo sharing website, web services suite, and online community platform was one of the earliest Web 2.0 applications. In addition to being a popular website for sharing personal photographs, the service is widely used by bloggers as a photo repository. Flickr’s popularity has been fueled by its innovative online community tools that allow photos to be tagged and browsed by folksonomic means, a social/collaborative way to create and manage tags for content, in contrast to traditional subject indexing, in which content is fit to subjects predetermined by experts (Vander Wal, 2007). In Flickr, metadata are generated by not only experts but also creators and consumers of the content. Folksonomies became popular on the Web around 2004, with social software applications such as social bookmarking or annotating photographs. Typically, folksonomies are Internet-based, although they are also used in other contexts. Folksonomic tagging is intended to make a body of information increasingly easy to search, discover, and navigate over time.
As folksonomies develop in Internet-mediated social environments, users can discover who created a given folksonomy tag, and see the other tags that this person created. In this way, a folksonomy user may discover the tag sets of another user who similarly interprets and tags content. The result is often an immediate and rewarding gain in the user’s capacity to find related content (a practice known as pivot browsing). Part of the appeal of folksonomy is its inherent subversiveness: Compared to the choice of the search tools that websites provide, folksonomies can be seen as a rejection of the search engine status quo in favor of tools that are created by the community. Obviously, in addition to being a place to share photos, Flickr is a great source of media form students’ multimedia productions.
Blogger
Brock has used this one, putting his class blog (www.5th-teacher. blogspot.com) up on the screen, with images, examples, links to other resources, related news events, goings on in the class, his teaching manifesto, and global descriptions of assignments, as well as breakdowns of daily work. He also embeds his slide shows in the blog, along with video. This provides a resource for students to use both in class and outside of class. Because students have learned the format, and how to use pictures and other media from the Web, they have become proficient at creating reflective work and high-quality
multimedia productions. Blogger gets a bad rap by some, but you can limit the audience of student blogs by closing them off from the world feature and selecting viewers by inviting specific people. This also allows the teacher to access the blog if there is questionable content for classroom blogs “gone rogue.â€
SlideShare
This Web application is great for getting students to see the opportunities of creating active multimedia products. Brock’s students created slide shows in PowerPoint, using images, text, and animation and transition effects, then uploaded them to SlideShare. This allowed the class to create their own group (Washburn Introduction to Engineering Design [IED]) where they could see and comment on each others’ slides, as well as use the chat function. Students also use SlideCast, in which they enter and synchronize an MP3 with their presentation, so that both teachers and students can create music videos or even do voice-over narration for telling stories and performance (dramatic) readings. SlideShare also lets you one-click to Blogger, so that students may embed their slide show in their blog. A cool feature is the ability to link this into Facebook.
Google Suite
Google provides a nice suite of tools for educators and students. Often your students have computers with Internet access at home but lack productivity software, such as Microsoft Office, or free tools such as OpenOffice. Students can use the Google Suite to create word processing, slide shows, and spreadsheets. The impressive feature is that this suite is available online, so students with an Internet connection can work at home on the document they created at school. And as with other Web 2.0 applications, students may invite others to cowrite and produce documents here. This allows groups to work on the same paper, and it also tracks each person’s contributions as the document is created. We used Google Documents to collaborate on this chapter. In addition, Google Maps, Google Earth, and Google SketchUp, a three-dimensional modeling program, are other tools in the Google suite that deserve extra emphasis. Reading and writing practices are more engaging to students when tied to the creation of the places, people, and activities. Brock had students create scenes from the play A Raisin in the Sun using this tool. The class explored the role of place and lived space, and the way space influences how people feel, speak, and act. This high-tech diorama was reminiscent of the shoebox versions we sometimes made for fun or for school projects.
Zotero
Zotero, an easy-to-use yet powerful research tool, helps researchers gather, organize, and analyze sources (citations, full texts, webpages, images, andother objects), and share research results in a variety of ways. An extension of the popular open-source Web browser Firefox, Zotero includes the best parts
of older reference manager software (like EndNote)—the ability to store author, title, and publication fields, and to export that information as formatted references—and the best parts of modern software and Web applications (like iTunes and del.icio.us), such as the ability to interact, tag, and search in advanced ways. Zotero integrates tightly with online resources; it can sense when users are viewing a book, article, or other object on the Web, and—on many major research and library sites—find and automatically save the full reference information for the item in the correct fields. Since it lives in the
Web browser, it can effortlessly transmit information to, and receive information from, other Web services and applications; because it runs on one’s personal computer, it can also communicate with software running there (e.g., Microsoft Word). It can also be used offline (e.g., on a plane, in an archive without Wi-Fi).
Scribd
This document-sharing community and self-publishing platform enables anyone to publish easily, distribute, share, and discover documents of all kinds. You can submit, search for, and comment on e-books, presentations, essays, academic papers, newsletters, photo albums, school work, and sheet music. A powerful feature of this tool is that you can upload documents in many different formats, including Microsoft Word, Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF), plain text, hypertext markup language (HTML), PowerPoint, Excel, OpenOffice, Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG), and many other formats. Once your documents are uploaded, you can embed them in a blog, Facebook profile, or other external websites, with your fonts, images, and formatting fully intact. Each document hosted at Scribd has its own unique uniform resource locator (URL), and you have unlimited storage, so you can
upload as many documents as you like. Once these are up, they are also available for fast indexing by Google and other major search engines, so that your content can be found in simple searches. You can keep certain documents private or share with a limited number of friends, and you can automatically convert published content into PDF, Word, and plain text. What is engaging for young writers is that not only can they publish widely but they also can see how many people have viewed their documents by location. Through Google you find documents similar to your own, as well as connect with a community of writers working in the same content area, enabling feedback and dialogue about your documents yet allowing you to retain full copyright under Creative Commons licenses.
Other Web 2.0 Resources
Space limits preclude a more elaborate listing of the multitude of other Web 2.0 sites. We recommend that readers of this chapter peruse the following briefly annotated list of other sites promoting multimodal literacies:
• Digg. A community-based, popular news article website, where news stories and websites are submitted by users, then promoted to the front page through a user-based ranking system.
• bubbl.us. An online brainstorming tool that students and teachers can use to create colorful mind maps online, share maps and collaborate with friends, embed mind maps in blogs or websites, e-mail and print maps, and save maps as images.
• BigHugeLabs.com. A tool that makes using Flickr a lot more interesting by capitalizing on the site’s existing functionality. Dozens of toys, games, and utilities allow you, for example, to create a magazine cover from a selected Flickr photo, create a motivational poster, and access huge amounts of user    data (FlickrDNA).
• Photoshop Express. An application providing two gigabytes of storage to which you can link in your blogs or websites. You can edit images on the fly without having to up/download them each time or move from computer to computer, and you are just a login away from your library of photos.
• SoundJunction. A site where users can take music apart and find out how it works, create music, find out how other people make and perform music, learn about musical instruments, and look at the backgrounds of different musical styles.
• del.icio.us. (pronounced like the word delicious). A social bookmarking Web service for storing and sharing data with more than 3 million users and 100 million bookmarked URLs.
• Ning. A site that enables the creation of one’s own social network, designed to compete with sites like MySpace and Facebook, by appealing to users who want to create networks around specific interests, or who have limited technical skills.
• VoiceThread. A versatile online media album that can hold essentially any type of media (images, documents, and videos) and allow people to make comments in five different ways—using voice (with a microphone or telephone), text, audio file, or video (with a webcam)—and share them with anyone they wish.
• Many Eyes. A tool for the visual representation of data that makes sharing data creative and fun, while tuning students into the relation between information presentation and interpretation.
• Scratch. A designing tool with a language that makes it easy to create interactive stories, animations, games, music, and art.
Classroom Vignettes of Practices with Technologies and Literacy
Junior High “Intervention†Class
We have studied our reading/writing intervention class in a suburban community of the Twin Cities for 3 years (O’Brien, Beach, & Scharber, 2007). The class uses a Literacy Lab setting with a reduced enrollment target of 15 students, previously assessed as struggling in reading, and mentored by two
teachers, both of whom hold K–12 reading licenses. The class meets once a day in a block scheduling format, with 93-minute class periods. The curriculum juxtaposes traditional engagement activities with “new literacies†activities. For example, on the side of more traditional interventions, students use
the Scholastic READ 180 program, read and discuss young adult novels as a group, and dramatize the texts and a range of activities to integrate reading and writing. They also engage in strategies instruction, such as the use of mind mapping and various activities designed specifically to help students achieve competence on state language arts standards and high-stakes assessments. On the new literacies side, using various technology tools, the students engage in writing activities, such as producing stories, comic books (using Comic Life), wikis (in Moodle) and poetry writing. They write journal responses to their reading and construct PowerPoint presentations about topics, such as their favorite video games or young adult novels, and share their poetry or story writing. They plan, design, and perform radio plays (using GarageBand for background tracks and sound effects). Recently, students completed placebased projects in which they used VoiceThread to publish photos of important places in their school, complete with audio or print commentaries. They publish their writing in the school district Moodle site. Some of the students also participate in afterschool computer gaming sessions. In the new literacies realm, the teachers include practices in which students engage to explore ideas, construct a classroom community, and develop agency in meeting personally relevant goals.
Media Class Rhythm and Flow Unit
This was the first unit that Brock created after transitioning from a language arts teacher to a media specialist. He found that the units he taught as a language arts teacher were still very applicable to the standards and benchmarks in media technologies when it came to teaching media or print texts, or the many opportunities that arise as a result of having access to computers. As a media specialist, Brock tried to link the media and technology activities to improvement in reading and writing. For example, he included Reading Friday, in which students had to create a music business persona/image, describe their style of music, and choose lyrics that they would perform and record into Garage Band. GarageBand is one option. Students could also use one of the Web-based products we have discussed. So the students took print texts—poems, paragraphs, dialogue, and lyrics they liked—and recorded themselves reading as a track on the music software. They also recorded outtakes, or descriptions of the experiences, and rated their oral interpretation performances. After students had shared their tracks with Brock, they began to practice putting a beat and music behind the tracks. This enabled a thorough interpretation and exploration of voice and oral expression. Students who had never really thought about the qualities of the voices in the narratives (e.g., the tone, theme, pitch, volume, emphasis in elongation and breaks) could better hear and understand dramatic pauses, tone and volume changes, diction and word choices, as well as format, organization, and punctuation. This activity began to make a difference in students’ understanding of these concepts. As students began exploring pauses work, changing and emphasizing words, assonance, and resonance in rhyme structures, they were really looking at oral reading and fluency, and reading in general, in a much deeper and more playful way. Students then took photos and made their CD covers, using image manipulation software; they made their own liner notes and wrote their own copy for advertising; they conceptualized a MySpace design (because they were not permitted access to MySpace) and created tours, clothing, and so on. It turned into a game about being in the music business. This unit, which had originally been intended as a week-long reward for the kids, so engaged students as they performed their lyrics and created their music careers that Brock extended it for 2 weeks.
What are “best practices†in these scenarios? First, students engage in activities, using technologies that support both the local curriculum and state standards. Rather than considering technologies and innovation as replacements for more traditional instructional and learning, the technologies provide
more effective ways to engage students. Second, best practices dictate that the technologies enhance teaching and learning by providing access to media and enabling students to use various modalities to explore and publish ideas. Third, although we can already see a future in which digital literacies replace traditional print literacies, for now, given the realities of standards, print-centric assessments, and, particularly the predominately print-based curricula, best practices explore ways to bridge print and digital literacies effectively. Fourth, the notion of best practices, which we typically associate with teaching or facilitating learning, should be extended to include practices related to supporting infrastructures and increasing funding for technologies that do enhance teaching and learning.
Future Directions and Best Practices for Engaging Students in Literacy with Technology
Clearly, the future will bring a wider range of more accessible digital tools. What started as the Web 2.0 phenomenon will continue at a rapid rate as the analog television bandwidth is purchased by Web Portals, such as Google, to provide faster access to more and more data from small personal communication devices—things that we used to call “phones.†As shown by current studies from the Pew Internet and American Life project, youth will continue to use more media and engage in more media multitasking or multimediating. As more young people have access to these tools, the digital divide will persist but not be as defined. As educators, we will slowly but surely start to redefine learners based on the experiences these young people have daily in the mediasphere, and the way their brains are changing as result. Similarly, we will start to redefine literacy more in line with the new literacies practices in which youth engage outside of school, and to think of better ways to connect out-of- school and in-school experiences with technologies and literacy.
Given the frameworks briefly described in this chapter for understanding technology-enabled or enhanced texts and new literacies practices, what are some possible practices that will not only produce more engaged and better readers and writers, as traditionally defined, but also facilitate practices
that improve intertextual, intermedial, and multimodal understanding? We briefly outline some of these realizing that practices, they are morphing as we write, and that new ones will have emerged even before this chapter is published. We offer these not so much as static examples but as ways of thinking about best practices in the milieu of new and emerging technologies, and new literacies and literates. We want fellow educators to think in novel ways about how these new technologies may improve literacy practices, not because of their technical features, but because they are engaging. Although it is over simplistic to state that technologies are worthwhile simply because they are motivating, we might cautiously state that technologies are engaging because they often incorporate aspects of play, are pleasurable, and are associated with leisure time outside of school. We also argue that good technology can guide and extend students’ knowledge of the world and their relationship to it, and that the software and appliances it inhabits are means for guidance, creativity, and production. Here are some recommended practices as we to end this decade and head into the next.
Engaging Readers and Writers
Young people should have access to curricula and learning opportunities in which reading and writing strategies instruction is not always the focus; rather the focus is to provide high-interest engaging activities that allow young people to accomplish goals using a range literacy tools and practices, many of them enabled by technology. Young people can become very strategic about what tools they use and how they use them to engage in practices that produce personally relevant outcomes. Learners need to be strategic, but they do not always benefit most from being taught strategies. And, as we noted, it is quite possible that the learners we are trying to engage are harder to engage because of their experiences in the mediashpere. In Brock’s teaching, texts aren’t necessarily print texts; rather, they are multimodal messages (Dubbels, 2008). For example, Brock has even used allegorical paintings and text as movement activities and multimodal analogues to decoding and propositional levels of comprehension.
Connecting with Out-of-School Literacies
As educators, we should make a more concerted effort to connect school instructional practices and curricula to out-of-school practices. Literate practices involved in activities such as instant messaging, creating and reading images, authoring webpages, and participating in social networks are ignored, devalued, or even feared in schools. In contrast, students engagement in strategies instruction, skills instruction, and reading textbooks and answering questions is common. Although these traditional activities and assessments are important, and more directly tied to valued outcomes, such as performance on high-stakes tests, they are increasingly disconnected from the new literacies skills, knowledge, and abilities that youth use the most, and they are simply not as engaging as many of the digital literacies practiced outside of school. The digital tools, and the practices they support, some of
which we present shortly, are not intended to turn youth completely away from traditional academic reading and learning; rather, they are intended to engage them in novel ways with important content and learning tasks. The goal, as we noted, is to engage students in these practices, to improve their
learning, and to connect the learning to personally relevant goals.
Taking Advantage of Multimodality
Traditional print materials, such as textbooks, have changed little over the last 150 years, and they have performed admirably as the staple of the curriculum. But given the range of teaching and learning tools enabled by new and emerging technologies, print materials alone are increasingly inadequate, not
to mention uninteresting, to young people. Students are increasingly able to use a range of tools to compose and to understand complex ideas, to convey beliefs and emotions, and to share their creations in print, visual, aural, and even tactile and kinesthetic forms. The most straightforward practice to capitalize on the multimodality of digital texts is simply to make the tools available (e.g., computers, digital cams and audio recorders, multimedia authoring tools, Web authoring tools, Web 2.0 tools) and provide practice in using them. A more involved approach is to think systematically of multimodal
options for existing tasks and assignments (e.g., a media inquiry project in place of a report; a blog in place of a term paper), and to provide for students a choice in the modalities and tools they use. David and his colleagues did just this in the Literacy Lab at Jeff High School (O’Brien, 2006; O’Brien, Springs, & Stith, 2001) when they reconstructed an entire literacy curriculum to take advantage of a multimedia lab they set up.
Examining Stances toward Technology
Ideally, to construct digitally enabled curricula, youth need educators who are either capable of using the technologies or open to learning them (often with support of students!) and connecting the technology tools to literacy practices. Taking new stances requires new attitudes and familiarity with the frameworks we have briefly overviewed (e.g., frameworks in which texts are multimodal representations rather than just print, and reading and writing are socially and culturally embedded practices that can be enabled with digital tools). Prensky’s (2001) characterization of digital natives (the students) and digital immigrants (teachers who did not grow up with the technologies that students use adeptly) is a useful, albeit forced, binary that speaks to stance. Digital immigrants need to be willing to jump into the fray and start to use the technologies that their students know. The practical side of this
immersion is that teachers who use the technologies can understand how these tools enable teaching and learning; the more affective dimension is that the actualizing digital immigrants see the value of the tools and feel good about their own competence in using them.
Resources
Further Reading
Beach, R. (2006). Teachingmedialiteracy.com: A resource guide to links and activities. New
York: Teachers College Press. Available online at teachingmedialiteracy.com.
Burn, A., & Durran, J. (2007). Media literacy in schools: Practice, production and progres-
sion. London: Paul Chapman.
Coiro, J., Knobel, M., Lankshear, C., & Leu, D. J. (Eds.). (2008). The handbook of research
in new literacies. New York: Erlbaum.
Kist, W. (2005). New literacies in action: Teaching and learning in multiple media. New
York: Teachers College Press.
Websites
—Editlib. The EdITLib Digital
Library is a repository of peer-reviewed and published articles and papers on the
latest research, developments, and applications related to all aspects of educa-
tional technology and e-learning.
—The Assembly on Computers in English is a long-standing
assembly of the National Council of Teachers of English and is a nonprofit orga-
nization of English language arts teachers and teacher-educators dedicated to
intelligent technology integration into the English language arts.
—IRA Focus on Technology: IRA
Programs and Resources is a link to resources of the International Reading
Association site, designed to help educators support students in the new litera-
cies of information and communication technologies, as well as to help teachers
who want to become more proficient in using the technologies. The resources
include publications, online resources, and meetings and events that support
the use of technologies and literacy.
References
Alvermann, D. E., Moon, J. S., & Hagood, M. C. (1999). Popular culture in the classroom: Teaching and researching critical media literacy. Newark, DE: International Reading Association.
Beach, R., & O’Brien, D. G. (2008). Teaching popular culture texts in the classroom. In J. Coiro, M. Knobel, C. Lankshear, & D. Leu (Eds.), Handbook of research on new literacies (pp. 775–804). New York: Erlbaum.
Clark, A. (2003). Natural born cyborgs? In J. Brockman (Ed.), The new humanists (pp. 70–77). New York: Barnes & Noble.
Coiro, J., & Dobler, E. (2007). Exploring the online reading comprehension strategies used by sixth-grade skilled readers to search for and locate information on the Internet. Reading Research Quarterly, 42(2), 214–257.
Coiro, J., Knobel, M., Lankshear, C., & Leu, D. J. (Eds.). (2008). The handbook of research on new literacies. New York: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Cope, B., & Kalantzis, M. (Eds.). (2000). Multiliteracies: Literacy learning and the design of social futures. London: Routledge.
Dubbels, B. R. (2008). Video games, reading and transmedial comprehension. In R. E. Ferdig (Ed.), Handbook of research on effective electronic gaming in education (pp. 251–276). Hershey, PA: IGI Global.
Evans, E., & Po, J. (2007). A break in the transaction: Examining students’ responses to digital texts. Computers and Composition, 24, 56–73.
Foehr, U. G. (2006). Media multitasking among American youth: Prevalence, predictors, and pairings. Menlo Park, CA: Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation.
Graesser, A. C., Millis, K. K., & Zwaam, R. A. (1997). Discourse comprehension. Annual Review of Psychology, 48, 163–189.
Hague, S. A., & Mason, G. E. (1986). Using the computer’s readability measure to teach students to revise their writing. Journal of Reading, 30(1), 14–17.
Hobbs, R. (2007). Reading the media: Media literacy and high school English. New York: Teachers College Press.
Jewitt, C., & Kress, G. (Eds.). (2003). Multimodal literacy. New York: Peter Lang.
Kamil, M. L. (1982). Technology and reading: A review of research and instruction. In J. A. Niles & L. Harris (Eds.), New inquiries in reading research and instruction. Thirty-first yearbook of the National Reading Conference (pp. 251–260). Rochester, NY: National Reading Conference.
Kamil, M. L., Intrator, S., & Kim, H. S. (2000). Effects of other technologies on literacy and literacy learning. In P. M. M. Kamil, P. D. Pearson, & R. Barr (Eds.),
Handbook of reading research (Vol. 3, pp. 773–788). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kist, W. (2005). New literacies in action: Teaching and learning in multiple media. New York: Teachers College Press.
Knobel, M., & Lankshear, C. (Eds.). (2007). A new literacies sampler. New York: Peter Lang.
Kress, G. (2003). Literacy in the new media age. London, UK: Routledge.
Kress, G., & Van Leeuwen, T. (2001). Multimodal discourse: The modes and media of contemporary communication. London: Edward Arnold.
Lankshear, C., & Knobel, M. (2003). New literacies: Changing knowledge and classroom learning. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press.
Leander, K. M. (2007). “You won’t be needing your laptops todayâ€: Wired bodies in the wireless classroom. In M. Knobel & C. Lankshear (Eds.), A new literacies sampler (pp. 25–48). New York: Peter Lang.
Lenhart, A., Madden, M., Macgill, A. R., & Smith, A. (2007). The use of social media— from blogging to online social networking to creation of all kinds of digital material—is central to many teenagers’ lives. Washington, DC: Pew Internet and American Life Project.
Leu, D. J. (2000). Literacy and technology: Deictic consequences for literacy education in an information age. In M. L. Kamil, P. Mosenthal, P. D. Pearson, & R.
Barr (Eds.), Handbook of reading research (Vol. III, pp. 743–788). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
McEneaney, J. E. (2006). Agent-based literacy theory. Reading Research Quarterly, 41(3), 352–371.
Miller, P. (2005). Web 2.0: Building the new library. Ariadne, 45.
New London Group. (1996). A pedagogy of multiliteracies: Designing social futures. Harvard Educational Review, 66(1), 60–92.
O’Brien, D., Beach, R., & Scharber, C. (2007). “Struggling†middle schoolers: Engagement and literate competence in a reading writing intervention class. Reading Psychology, 28(1), 51–73.
O’Brien, D., & Scharber, C. (2008). Digital literacies go to school: Potholes and possibilities. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy, 52(1), 66–68.
O’Brien, D. G. (2006). “Struggling†adolescents’ engagement in multimediating: Countering the institutional construction of incompetence. In D. E. Alvermann,
K. A. Hinchman, D. W. Moore, S. F. Phelps, & D. R. Waff (Eds.), Reconceptualizing the literacies in adolescents’ lives (pp. 29–46). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
O’Brien, D. G., & Bauer, E. (2005). New literacies and the institution of old learning. Reading Research Quarterly, 40, 120–131.
O’Brien, D. G., Springs, R., & Stith, D. (2001). Engaging at-risk students: Literacy learning in a high school literacy lab. In E. B. Moje & D. G. O’Brien (Eds.), Constructions of literacy: Studies of teaching and learning in and out of secondary schools (pp. 105–123). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Pearson, P. D. (2004). The reading wars. Educational Policy, 18(1), 216–252.
Prensky, M. (2001). Digital natives, digital immigrants. On the Horizon, 9(5). Accessed April 1, 2008, from www.marcprensky.com/writing/Prensky%20-%20digital%20 natives,%20digital%20immigrants%20-%20part1.pdf.
Reinking, D., McKenna, M., Labbo, L., & Kieffer, R. (Eds.). (1998). Handbook of literacy and technology: Transformations in a post-typographic world. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Restak, R. (2003). The new brain: How the modern age is rewiring your mind. New York: Rodale.
Roberts, D. F., Foehr, U. G., & Rideout, V. J. (2005). Generation M: Media in the lives of 8–18 year-olds. Menlo Park, CA: Kaiser Family Foundation.
Vander Wal, T. (2007). Folksonomy Coinage and Definition. Retrieved October 26, 2007, from www.vanderwal.net/folksonomy.html.
Xiong, C., & Relerford, P. (2008, January 13). A minor walkout in Facebook flap. Minneapolis Star Tribune. Accessed October 24, 2008, at www.startribune.com/local/ west/13677002.html.